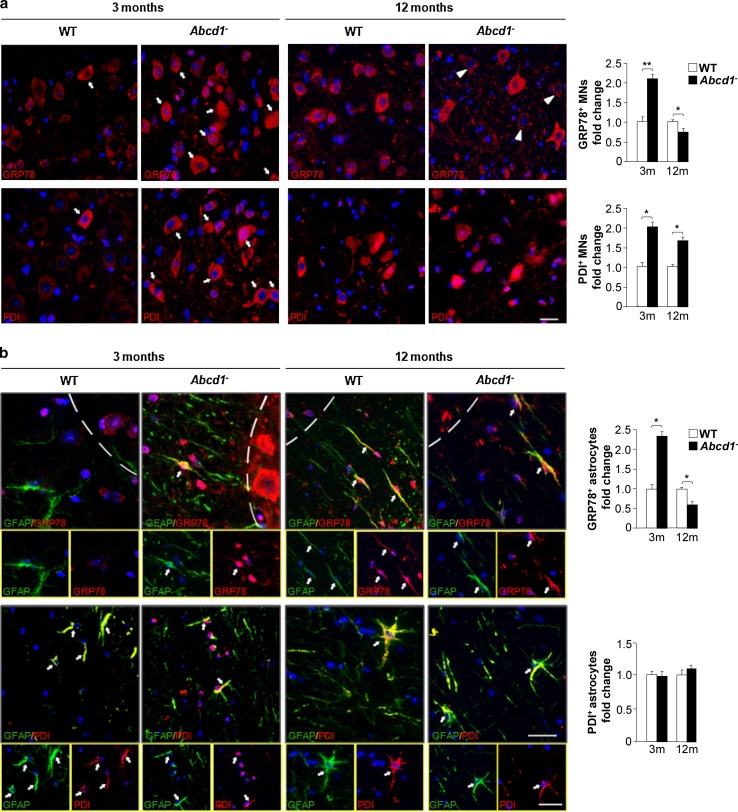
Fig. 3.
The UPR is primarily induced in motor neurons and astrocytes during X-ALD pathogenesis. a Immunofluorescence of GRP78 and PDI in spinal cord sections of WT and Abcd1 − mice 3 and 12 months of age. Arrows indicate high amounts of GRP78 and PDI in motor neurons; Arrowheads denote motor neurons with low amounts of GRP78. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Scale bar 50 μm. b Dual immunolabelling of astrocytes (GFAP; green) with GRP78 or PDI (red) in spinal cord sections of WT and Abcd1 − mice 3 and 12 months of age. Positive cells are labelled with arrows, and the dashed-line stands for the limit between the grey- and white matter. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. The small panel below shows some double-positive astrocytes. Scale bar 25 μm. The histogram on the right represents the quantification of GRP78 and PDI fluorescence intensity normalized to WT mice in motor neurons (MNs) (a) and astrocytes (b). Values are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 4 samples per genotype and condition in a and b; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, Student’s t test)