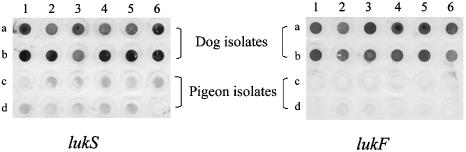
FIG. 1.
Dot blot analysis of genomic DNA from S. intermedius isolates with lukS and lukF probes. Spots a1 and a2, ITS-PCR type A; a3 and a4, ITS-PCR type B; a5 and a6, ITS-PCR type C; b1 and b2, ITS-PCR type D; b3 and b4, ITS-PCR type E; b5, ITS-PCR type F; b6, ITS-PCR type G; c1 and c2, ITS-PCR type H; c3 and c4, ITS-PCR type I; c5, ITS-PCR type J; c6 and d1, ITS-PCR type K; d2 to d5, ITS-PCR type L; and d6, negative control (Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium). All S. intermedius strains were included in dot blot hybridization analysis, but only two representative, randomly selected strains for each ITS-PCR type, with the exception of four strains for ITS-PCR type L and one strain each for ITS-PCR types F and G, are shown.