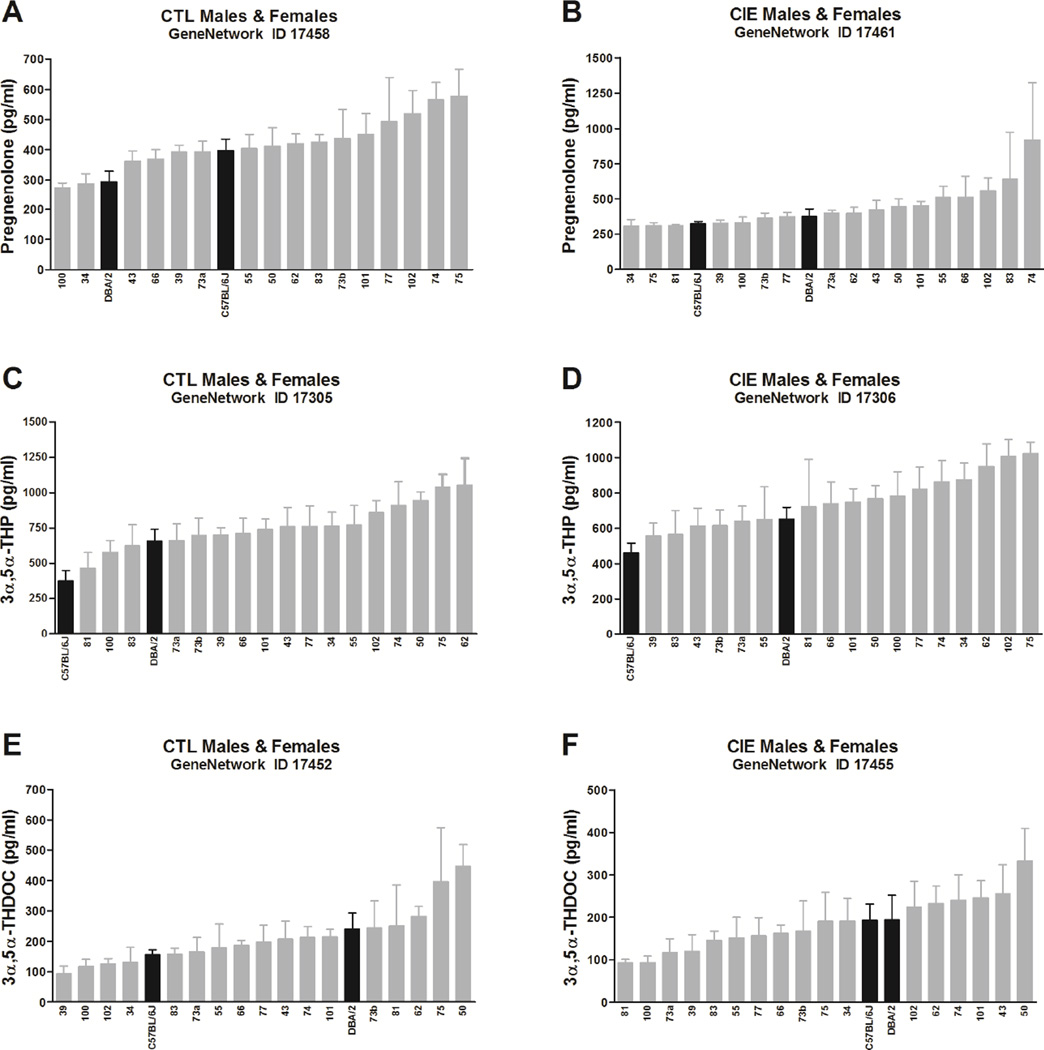
Fig. 1. Variation in basal pregnenolone (A–B), 3α,5α-THP (C–D), and 3α,5α-THDOC (E–F) levels across BXD strains.
Mice from each genotype received four cycles of chronic intermittent ethanol (CIE) vapor exposure (CIE group, B–D–F) or air exposure (CTL group, A– C–E) (16 h/day × 4 days, followed by 72-h withdrawal), alternated with 5-day drinking test cycles using a two-bottle (15% v/v ethanol vs. water) limited access (2 h/day) drinking model. Blood samples for neuroactive steroid assays were collected 72 h after a fifth CIE or air exposure cycle. Neuroactive steroid levels, assayed in all male and female cases, are expressed as pg/mL and are means ± SEM of values from 2–16 mice/strain/treatment. The x-axis reports the BXD strain number; C57BL/6J and DBA/2 are also indicated (black bars). Strains are plotted in order from the lowest to the highest levels for each of the neuroactive steroids. One-way ANOVA was used to estimate significant variation.