FIGURE 1.
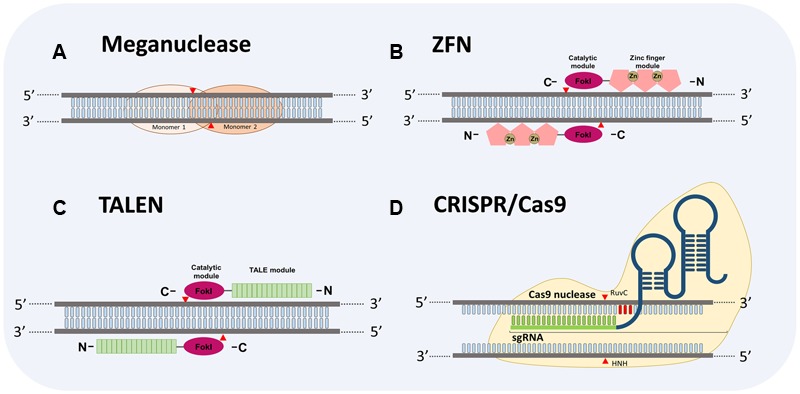
Schematic diagram depicting four Genome Editing Systems (GES) to target DNA. (A) Homodimers structure of a meganuclease system. (B) Zinc finger nuclease (ZFN) showing two monomers bound to DNA. The ZFN contains a catalytic FokI domain (ellipse in pink) and a zinc finger DNA-binding domain (DBD) (pentagons in rose). (C) Transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN) showing two monomers bound to DNA. Like ZFN, TALEN comprises a catalytic FokI domain (ellipse in pink). Light green rectangles represent the DNA bind domain containing the repeat variable di-residue (RVD) arrays of amino acids to recognize DNA specific sequences. (D) Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9) (CRISPR/Cas9). Typically CRISPR/Cas9 system comprises a Cas9 protein (depicted in light gold) with two nuclease domains, referred as HuvC and HNH, and a chimeric single guide RNA (sgRNA). The sgRNA consists of a CRISPR RNA (crRNA, 21 nucleotides in light green) to direct the Cas9 protein to the complementary sequences of the DNA target and a trans-activating crRNA (RNA sequence represented in dark blue) involved in the processing of pre-crRNA into a mature crRNA. Arrowheads in red indicate cleave sites to each GES.
