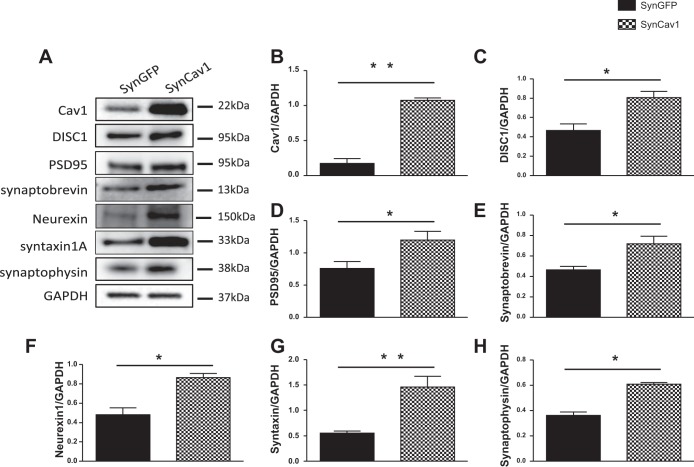
Fig. 5.
Neuron-targeted expression of caveolin-1 (Cav-1) enhances expression of disrupted-in-schizophrenia-1 (DISC1) and synaptic proteins in human differentiated primary neurons. The human neurons were differentiated from the Craig Venter 4a neuronal stem cells, which are derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Neurons were differentiated in differentiating media for 3–4 wk. After differentiation, neurons were infected by a lentivirus containing the Cav-1 driven by a synapsin promoter (HIV-synCAV1, or SynCav1) for 72 h. SynGFP served as control vector (109 viral particle from both vectors). Homogenates were immunoblotted for Cav-1, DISC1, PSD95, synaptobrevin, neurexin 1, syntaxin 1A, synaptophysin, and GAPDH (A). Quantification of Western blots showed overexpression of Cav-1 protein (B). SynCav1 also significantly enhanced the protein expression of DISC1 (C) and other synaptic proteins: PSD95 (D), synaptobrevin (E), neurexin 1 (F), syntaxin 1A(G), and synaptophysin (H). Representative blots are from n = 4 experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, SynCav1 vs. SynGFP.