Figure 10.
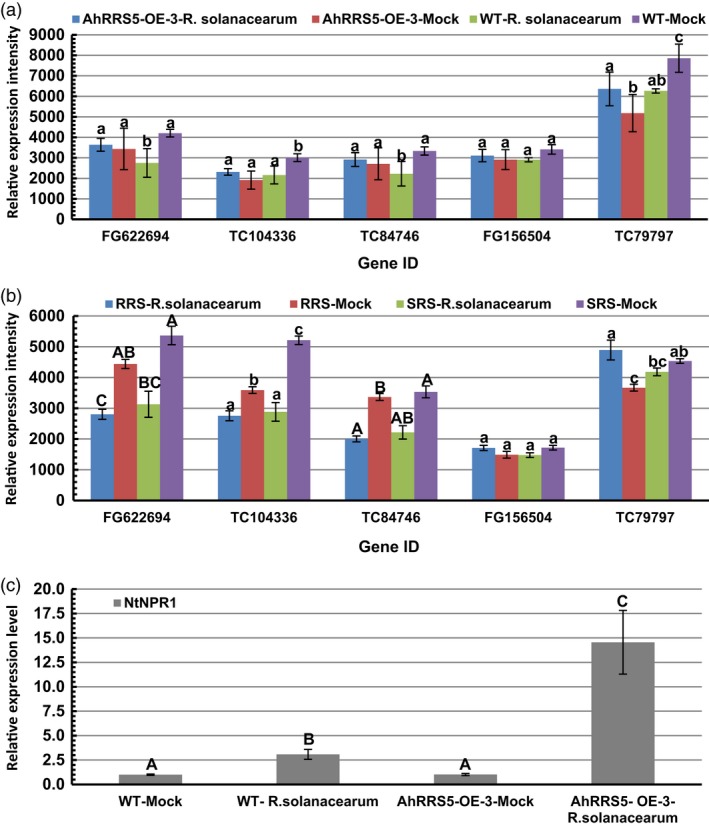
In silico and qPCR analysis of NDR1‐ and NPR1‐like gene expression upon inoculation with R. solanacearum. (a and b) Microarray data. (a) Expression of three NDR1‐like and two NPR1‐like genes. AhRRS5‐OE‐3‐R. solanacearum indicates tobacco CB‐1 cultivar transformed with AhRRS5 with inoculation; AhRRS5‐OE‐3‐Mock, transgenic CB‐1 without inoculation; WT‐R. solanacearum, CB‐1 with inoculation; WT‐Mock, CB‐1 without inoculation. (b) Down‐regulation of three NDR1‐like genes in varieties after inoculation. RRS ‐R. solanacearum indicates hyper‐resistant tobacco variety Yanyan 97 under inoculation; RRS‐Mock, hyper‐resistant variety Yanyan 97 without inoculation. SRS R. solanacearum, hypersusceptible variety Honghuadajinyuan with inoculation; SRS‐Mock, hypersusceptible variety Honghuadajinyuan without inoculation. FG622694,TC104336 and TC84746 are NDR1‐like genes; FG156504 and TC79797 are NPR1/NIM1‐like genes, respectively. (c) Transcript level of NtNPR1 gene in tobacco plants with or without inoculation with R. solanacearum through qRT‐PCR analysis. WT‐Mock and WT‐R. solanacearum, AhRRS5‐OE‐3‐Mock and AhRRS5‐OE‐3‐R. solanacearum indicate wild‐type tobacco without or with inoculation with pathogen, AhRRS5‐OE‐3 transgenic tobacco without or with inoculation with pathogen, respectively. Alphabets mark statistically significant differences between wild‐type and transgenic tobacco plants, by Student–Newman–Keuls test (lowercase differences indicate P‐value <0.05; uppercase differences indicate P‐value <0.01).
