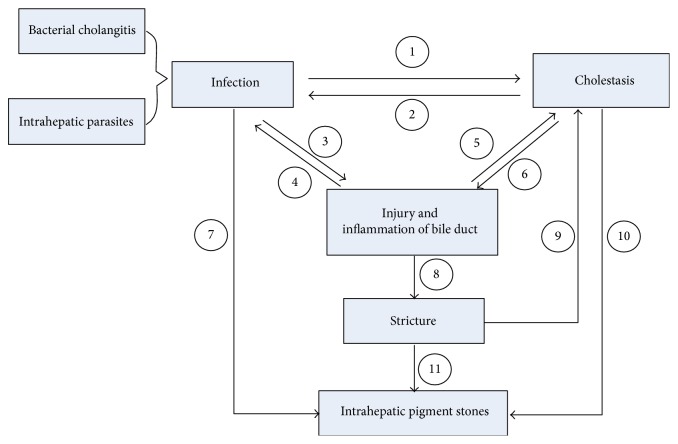
Figure 1.
Causes of intrahepatic pigments stones and their relationships. Infection, cholestasis, and stricture are the three main causes of intrahepatic pigment stones. ① Bacterial infection may influence the produce and transport of the bile and the worms or eggs of the parasites may lead to obstruction, resulting in cholestasis. ② It is easier for bacteria to invade when cholestasis. ③ Bacteria or worms as well as their secretions are easy to induce the injury and inflammation of bile duct. ④ Bacterial cholangitis is inclined to occur after the loss of protective effects of normal bile duct. ⑤ ⑨ The pressure inside the bile duct changes when there is injury, inflammation, or stricture of bile duct, leading to cholestasis. ⑥ Cholestasis means toxic bile acid accumulated to cause biliary walls injury and inflammation. ⑦ Bacteria produce relevant substances that may cause changes of the components in bile and finally deposit. ⑧ Prolonged inflammation may cause fibrosis of biliary walls, resulting in cholangitic stenosis. ⑩ Cholestasis provides time and place for the bile components deposited and then forms shaped stones. ⑪ The bile generates circumfluence and vortex above and below the stricture, providing additional power for small particles gathering.