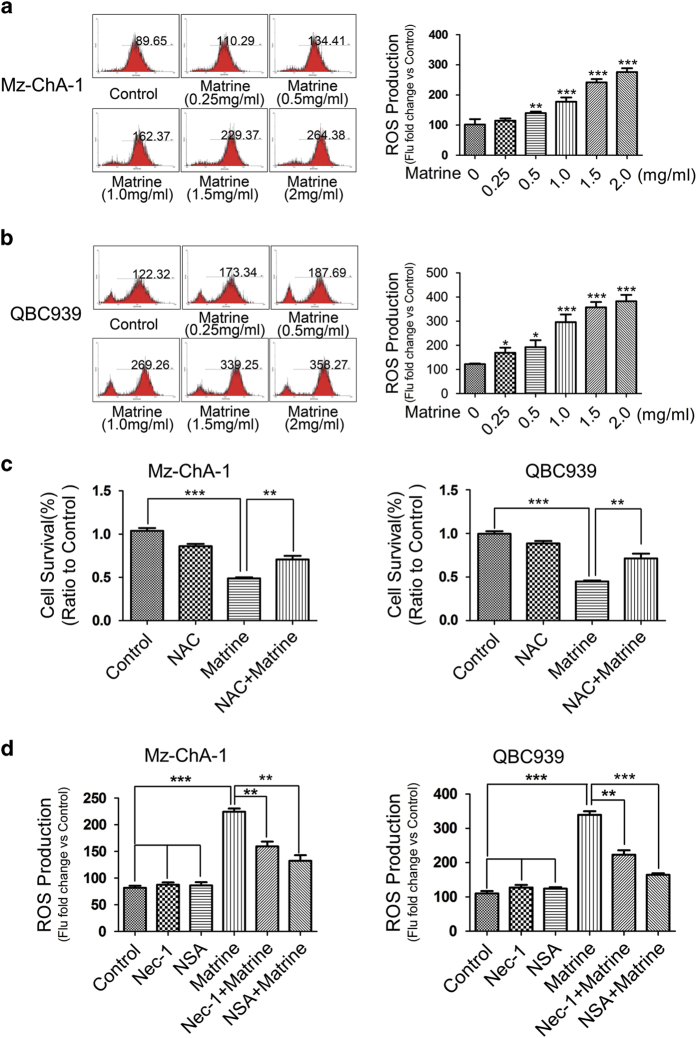
Figure 5.
ROS production stimulated by matrine/RIP3/MLKL signaling contributed to matrine-induced necroptosis. (a and b) Matrine increased the ROS levels of Mz-ChA-1 and QBC939 cells in a dose-dependent manner. Cells were treated with different concentrations of matrine (0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 1.5 and 2 mg/ml) for 24 h, then the ROS production was measured by flow cytometry. (c) Matrine-induced cell death was suppressed by ROS scavenger NAC. Cells were pre-treated with NAC (5 mM) for 3 h, and then treated with matrine (1.5 mg/ml) or vehicle for 48 h. Cell viability was assessed by MTT assay. (d) ROS production elevated by matrine were suppressed by Nec-1. Cells were pre-treated with necroptosis inhibitor Nec-1 (20 μM) or NSA (20 nM) for 2 h, and then treated with matrine (1.5 mg/ml) or vehicle for 24 h. ROS levels were detected by flow cytometry. All data were presented as the mean±S.D. from three independent experiments. Significant differences were indicated as *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 (assessed by Student’s t-test).