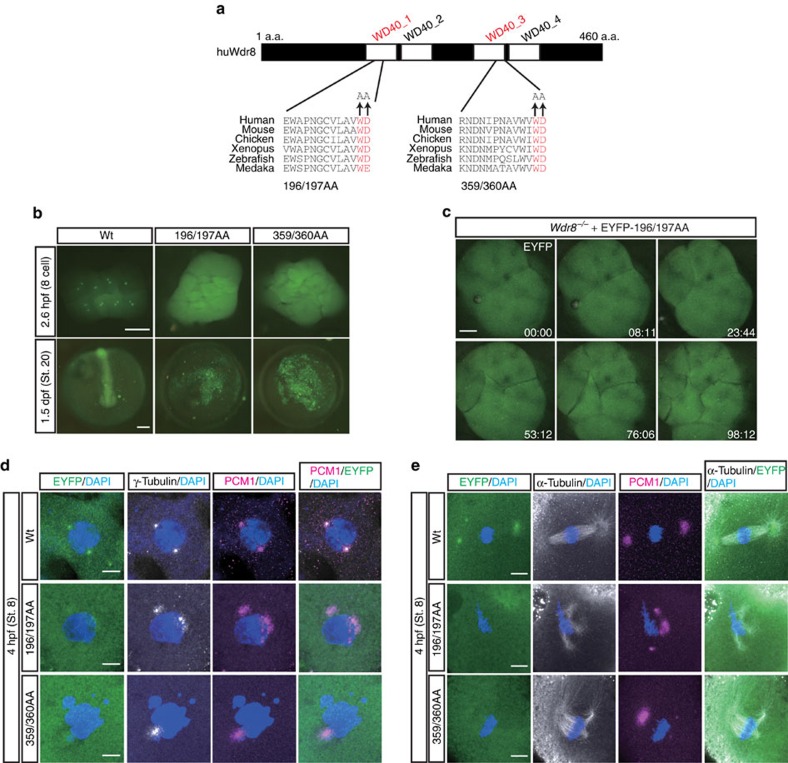
Figure 4. WD40 domains are essential for Wdr8 function.
(a) The conserved four WD40 domains in huWdr8. Mutations for WD mutant variants are denoted in red. (b) External phenotypes of WD mutant-injected Wdr8−/− zygotes and embryos. Note that both variants mostly localised in the cytoplasm (2.6 hpf), unable to rescue Wdr8−/− embryos (1.5 dpf). (c) Time-lapse images of EYFP-196/197AA localisation in Wdr8−/− blastomeres. EYFP-196/197AA weakly localised to the centrosome with multiple foci, which disappeared during cleavages. Time, min. (d,e), In comparison with EYFP–huWdr8 wild-type, expression of either mutant variant was unable to rescue abnormal PCM assembly (γ-tubulin/PCM1), multipolar mitotic spindles, and chromosome alignment defects. Scale bars, 200 μm (b), 100 μm (c) and 10 μm (d,e). Stages are denoted as hours/days post fertilisation (hpf, dpf) and the corresponding stage of WT are denoted in parentheses.