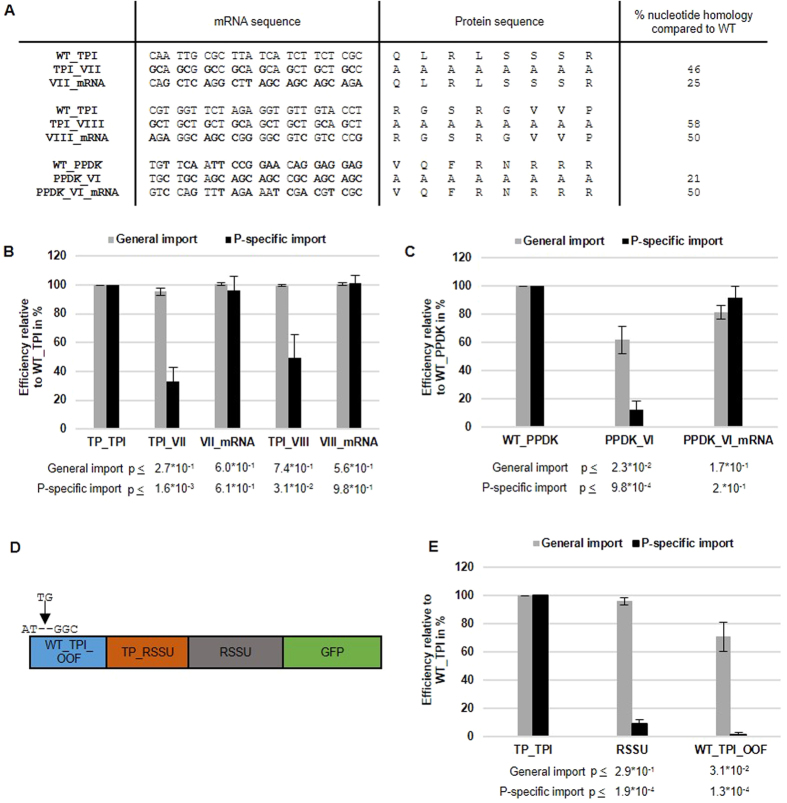
Figure 5. Mutations affecting the mRNA sequence but not the amino acid sequence of the transit peptides of TPI or PPDK do not affect P-specificity.
(A) Partial mRNA sequences and corresponding amino acid sequences from wild type TPs (WT_TPI, WT_PPDK), their alanine substitutions (TPI_VII, TPI_VIII, PPDK_VI) and the wobbled/codon switched mRNA (VII_mRNA, VIII_mRNA, VI_mRNA). Numerals indicate homology compared to WT in percent. (B,C,E) Quantification of GFP signals in transfected protoplasts by fluorescence microscopy. Expression pattern of GFP was categorized in general or P-specific import. Protoplasts were analyzed and statistics were performed as described in Fig. 3. p-values are indicated in the figure. Efficiency of P-specific and general import of TPI (n = 4) (B) or PPDK (n = 3) (C) in comparison to the alanine substitution mutants and mRNA mutations. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. (D) Chimeric construct of the nucleotide sequence of the TP of TPI fused in front of the coding region of full length RSSU-GFP. The nucleotide sequence of the TPI transit peptide contains a two nucleotide insertion at the start codon to produce an out of frame (OOF) shift resulting in a non-translatable mRNA sequence for the TPI TP followed by a translatable mRNA sequence for the full length RSSU. (E) Efficiency of P-specific and general import of the chimeric construct (n = 3).