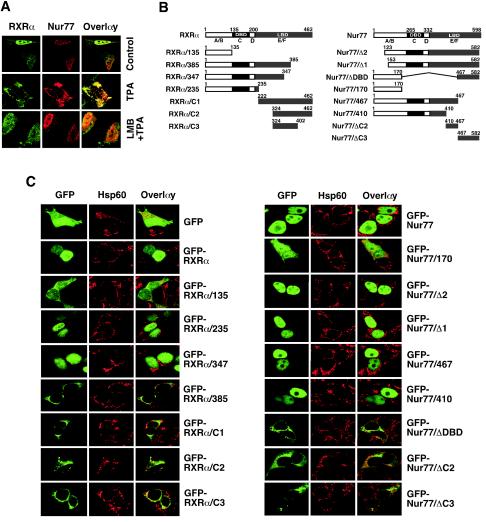
FIG. 3.
Identification of domains in RXRα and Nur77 required for their nuclear export. (A) Cytoplasmic localization of RXRα/Nur77 is mediated by CRM1-dependent nuclear export. LNCaP cells were treated with TPA (100 ng/ml) in the absence (control) or presence of LMB (2.5 ng/ml; Sigma) and analyzed by confocal microscopy as described for Fig. 1C. About 80% cells showed the cytoplasmic localization of RXRα and Nur77 after treatment with TPA, whereas >50% of cells showed nuclear localization of RXRα and Nur77 when pretreated with LMB. One of two similar experiments is shown. (B) Schematic representations of RXRα and Nur77 mutants. The DBD, LBD, and A to F domains are indicated. (C) Analysis of subcellular localization of Nur77 and RXRα mutants. The indicated plasmids were transfected into HEK293T cells and analyzed by confocal microscopy as described in Fig. 1. More than 90% of transfected cells showed diffused distribution of GFP and GFP-RXRα/135. Nuclear localization of GFP-RXRα, RXRα/235, and RXRα/347 was found in 80, 85, and 60% of transfected cells, respectively. More than 90% of transfected cells showed exclusive cytoplasmic localization of RXRα/385, RXRα/C2, and RXRα/C3, whereas cytoplasmic localization of RXRα/C1 was found in 70% of transfected cells. Nuclear localization of GFP-Nur77 and its mutants, GFP-Nur77/Δ2, GFP-Nur77/Δ1, GFP-Nur77/467, and GFP-Nur77/410, was found in >90% of transfected cells, whereas cytoplasmic localization of GFP-Nur77/ΔDBD, cytoplasmic localization of GFP-Nur77/ΔDBD, GFP-Nur77/ΔC2, and GFP-Nur77/ΔC3 was observed in 80, 60 and 70% of transfected cells, respectively. One of four similar experiments is shown.