FIG. 10.
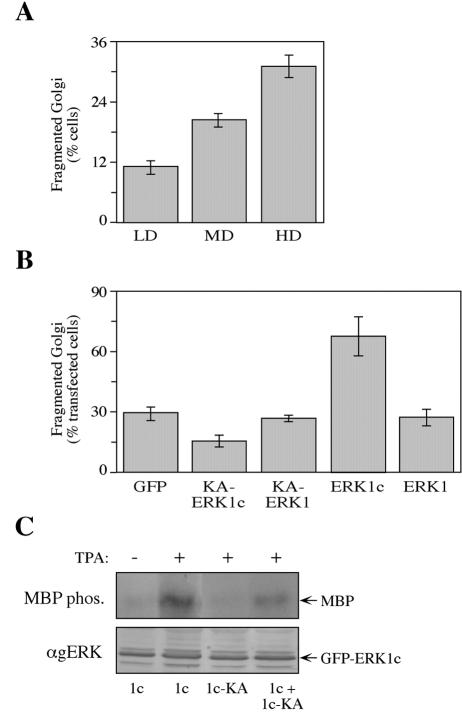
Inhibition of cell density-dependent Golgi fragmentation by the dominant-negative KA-ERK1c. (A) Golgi fragmentation increased with elevated cell density. HeLa cells were seeded on 18-mm microslides at low density (LD) (20,000 cell/well of a 12-well plate), medium density (MD) (60,000 cells/well), and high density (HD) (120,000 cells/well). Twenty-four hours after plating, the cells were fixed and stained with anti-p58 Ab. The percentage of cells with fragmented Golgi apparatus was determined by counting 200 cells in each slide. The values are the means ± standard errors (error bars) for three experiments. (B) Overexpression of KA-ERK1c inhibits cell density-dependent Golgi fragmentation. HeLa cells were seeded on 18-mm microslides at high density (120,000 cells/well) and transfected with GFP, GFP-KA-ERK1c, GFP-KA-ERK1, GFP-ERK1c, or GFP-ERK1. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were fixed and stained with anti-p58 Ab. The percentage of cells with fragmented Golgi apparatus out of cells expressing the exogenous construct is presented. The values are the means ± standard errors (error bars) for three experiments. (C) KA-ERK1c has a dominant-negative effect. HEK-293 cells were transfected with GFP-ERK1c (1c), GFP-KA-ERK1c (1c-KA), or HA-ERK1c together with GFP-KA-ERK1c (1c + 1c-KA). The cells were serum starved and stimulated with TPA (+) (250 nM, 15 min) or left untreated (−). After harvesting, the GFP proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP Ab, subjected to an in vitro MBP phosphorylation (MBP phos.) and concomitantly immunoblotted with anti-gERK Abs (αgERK) to confirm equal immunoprecipitation of the GFPs.