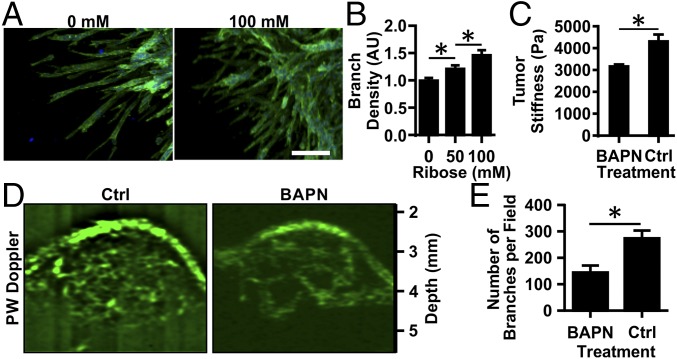
Fig. 2.
Matrix cross-linking alters angiogenic branching in vitro and in vivo. EC multicellular spheroids were embedded within 1.5-mg/mL collagen gels glycated with 0, 50, or 100 mM ribose. (A) Spheroids were fixed, stained for actin (green) and nuclei (blue), and imaged using confocal microscopy after 5 d. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (B) The number of branches per sprout length was counted, and data were normalized to the 0-mM ribose condition. AU, arbitrary units. (C) MMTV-PyMT mice were treated with BAPN to prevent collagen cross-linking or with vehicle (controls; Ctrl), and the equilibrium compressive moduli were measured using unconfined compression testing. (D) The tumor vasculature was visualized using ultrasound. (E) The number of visible vascular branches was quantified using the ImageJ Tubeness plugin. Data are presented as mean + SEM; *P < 0.05.