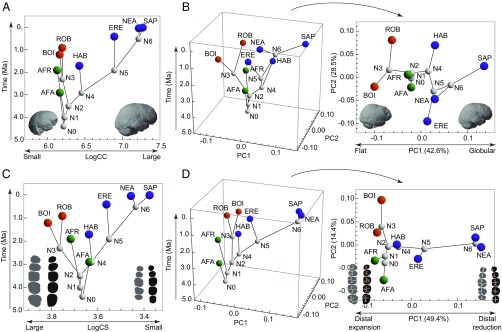
Fig. 2.
Variation in endocranial and dental size and shape through time. (A) Change in endocranial size (logarithm of cranial capacity, LogCC) over time showing extreme examples of variation. (B) PCA of endocranial shape variation over time (Left) and projection of PC1 and PC2 without time (Right). (C) Change in dental size (logarithm of centroid size, LogCS) over time. (D) PCA of dental shape variation over time (Left) and without time (Right). In A and B, the small and flat endocasts are the A. afarensis Sts 5 and P. robustus SK 1585 specimens, respectively. The large, globular endocast is a recent H. sapiens. Endocasts are in the same orientation as in Fig. 1. In C and D dental silhouettes representing large and distally expanded dentitions are based on the P. robustus specimens SK 13/14 (upper teeth) and SK 23 (lower teeth). Small and distally reduced dentitions are based on a recent H. sapiens. The orientation of teeth is the same as in Fig. 1. AFA, A. afarensis; AFR, A. africanus; BOI, P. boisei; ERE, H. erectus; HAB, H. habilis; NEA, H. neanderthalensis; ROB, P. robustus; SAP, H. sapiens.