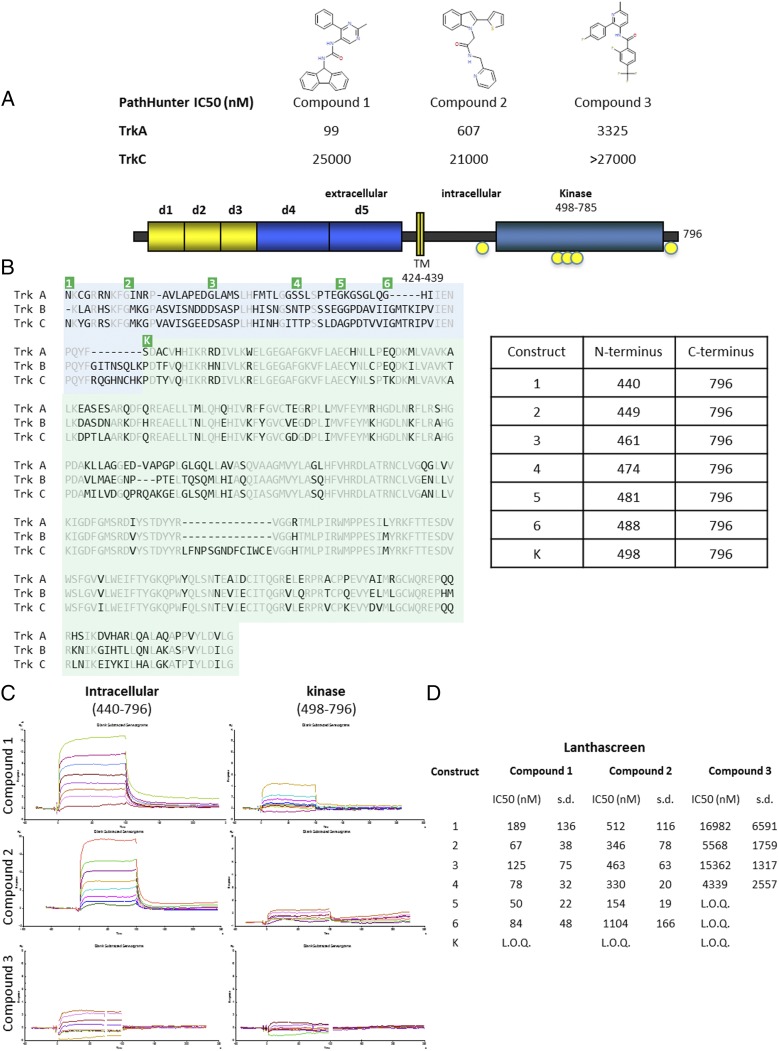
Fig. 1.
Activity and binding of compounds identified by ALIS screening. (A) The three compounds identified by ALIS screen and determined to be selective for TrkA over TrkC are shown. The IC50 values from the cell-based, PathHunter assay against TrkA and TrkC are given in nanomolars. Compound 3 did not inhibit at the highest concentration tested in the assay [limit of quantitation (LOQ) was > 27,000 nM in this assay]. (B) The schematic of full-length TrkA is shown at the top with domains indicated. Key phosphorylation sites are indicated in yellow circles. A sequence alignment is shown below for the intracellular region of TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC. Residues identical in all three sequences are colored gray. The kinase domain is shaded green and the JM region is shaded blue. The table on the right shows the residues that comprise each construct generated to test inhibition. The corresponding amino termini of the constructs are indicated on the sequence alignment in green. The constructs all extend to the natural carboxy-terminus of TrkA, followed by a hexahistidine tag for purification. Construct 1 starts immediately following the transmembrane helix. Each subsequence construct has an amino terminus closer to the kinase domain, which is indicated as construct K. (C) SPR binding traces of each compound to either the full intracellular region (construct 1) or the isolated kinase domain. (D) Lanthascreen assay of constructs with each of the three compounds. For each compound, a minimal construct can be inhibited by each inhibitor and all constructs longer than the minimal construct can also be inhibited by the compound. Construct 4 can be inhibited by all three compounds (LOQ was > 67,500 nM in this assay).