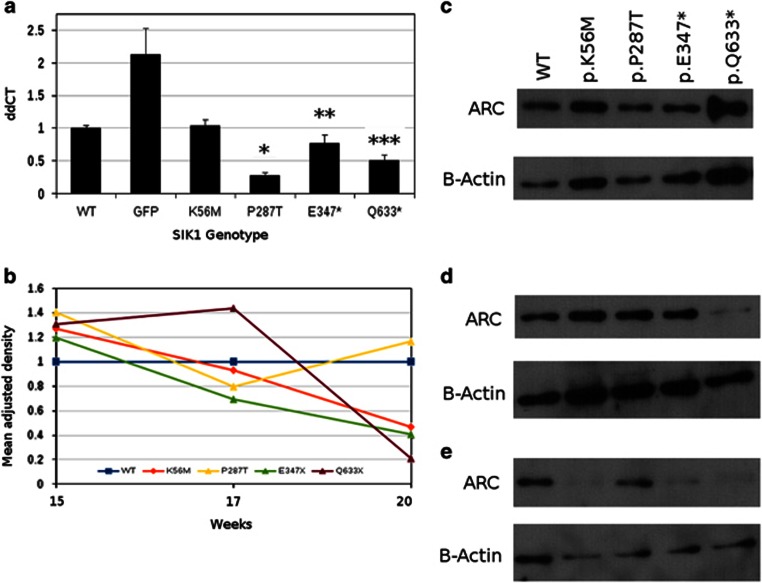
Figure 3.
Epilepsy-causing SIK1 sequence variations decreased ARC mRNA and protein levels. Semiquantitative reverse transcriptase-PCR of ARC was significantly reduced in all disease-causing mutants in 20-week fetal-derived primary neurons (a; *P=0.004; **P=0.02; ***P=0.0005) compared with neurons expressing wild-type SIK1. Neurons transfected with GFP were used as a vector control. There was an overall downward trend in ARC protein levels detected by western blot at 15, 17 and 20 weeks gestation in all SIK1 mutants compared with wild type. The p.(Glu347*) and p.(Gln633*) sequence variants had significantly (P=0.05 and P=0.007, respectively) decreased ARC protein levels compared with wild-type neurons at 20 weeks gestation (b). Representative western blots of ARC protein levels in human neurons at 15 weeks (c), 17 weeks (d) and 20 weeks gestation (e) normalized to β-actin.