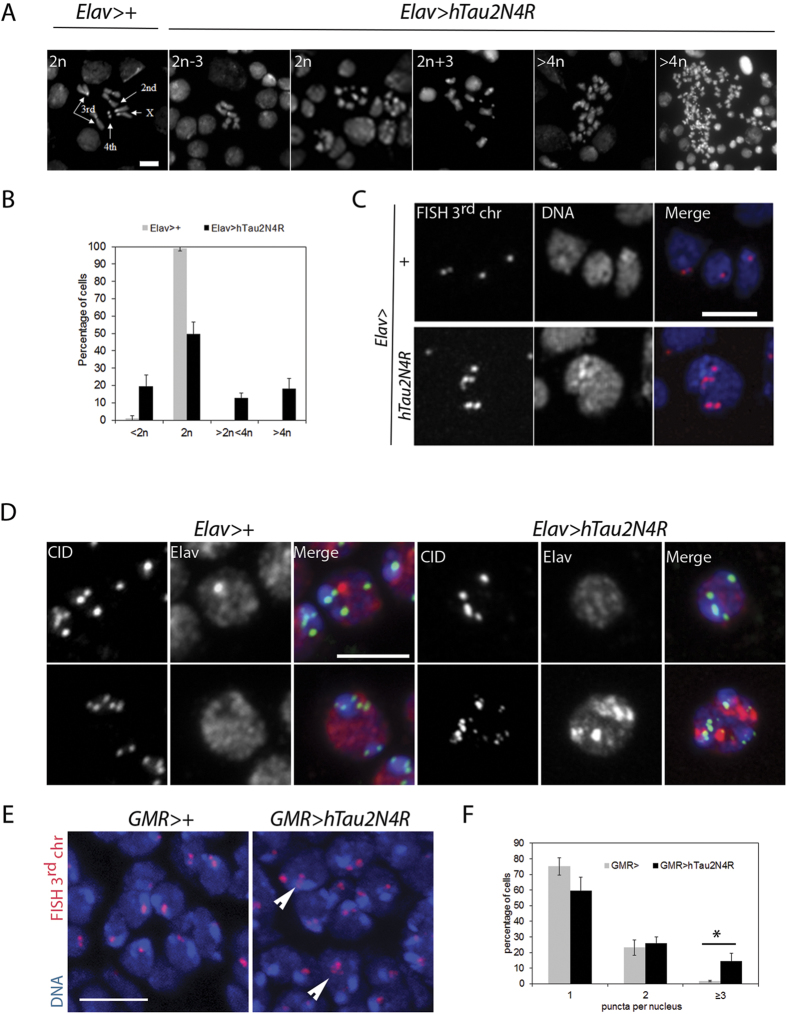
Figure 6. Aneuploidy generated by 4R-Tau expression in larval brains and post-mitotic pupal retinas.
(A) Metaphase spread from wild-type third instar larval brains showing the karyotype composed of 4 well identifiable chromosome pairs. Examples of diploid and aneuploid karyotypes following 4R-Tau expression during Drosophila development (Scale bar = 10 μm). (B) Quantification of the aneuploidy in wild type control (n = 206, mean ± SD) and 4R-Tau-expressing brains (n = 302, mean ± SD). (C) FISH experiment to detect the third chromosome Dodeca satellite in adult brains in wild-type and 4R-Tau adult flies. An aneuploid adult neuron in 4R-Tau adult brains with 5 third chromosomes is shown (Scale bar = 10 μm). (D) Detection of the CID/Cenp-A epitope to visualize all centromeres indicated the presence of different centromeric configurations in wild-type adult neurons. Example of adult neurons in brains with developmental 4R-Tau expression exhibiting a wild-type configuration (upper panels) and an aneuploid neuron showing the presence of 15 clear CID/Cenp-A foci (lower panels) (Scale bar = 5 μm). (E) Wild type and 4R-Tau-expressing pupal retinas were assayed for chromosome abnormalities using FISH to detect the third chromosome Dodeca satellite probe labeled with Cy3. Arrowheads indicate aneuploid cells. Scale bar = 5 μm. (F) Quantification of FISH foci in wild type and 4R-Tau expressing pupal retinas. 4R-Tau expressing animals contained significantly more nuclei with 3 or more foci, indicating an increase in aneuploidy. Unpaired two-tailed t-test, p = 0.0113.