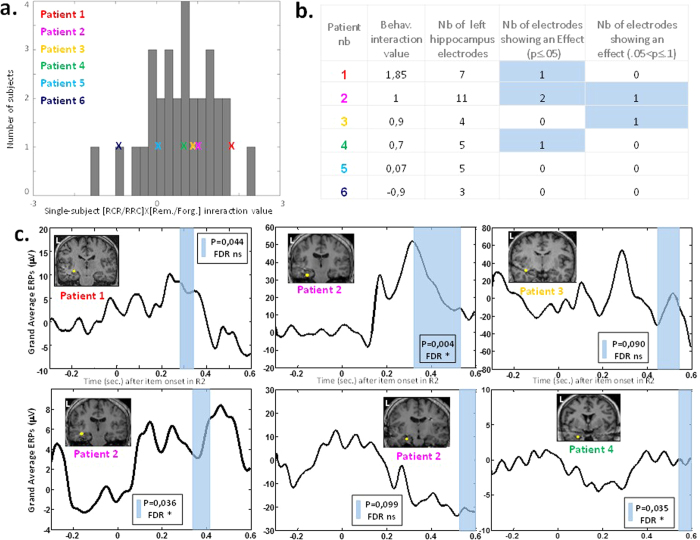
Figure 3. SEEG experiment revealed the contribution of hippocampus to CIPC before the behavioral response during the second rating.
(a) Patients’ individual interaction values belonged to the distribution of interactions observed in the normal population (N = 30 controls)19. (b) Table summarizing behavioral and SEEG results of each SEEG patient. Note that 6 out of 35 electrodes with a significant critical interaction, and that these effects were observed in each of the 4 patients showing a positive CIPC in their behavior (patients 1 to 4). (c) Paralleling behavior and fMRI, the interaction between condition and memory during rating 2 session was observed in contacts located in the vicinity (≤30 mm) of the fMRI peak of activation within the left hippocampus. Electrodes from 4 patients showed the predicted modulation of activity within temporal window (200–600 ms). For each electrode P-value computed with a non-parametric Monte-Carlo based permutation statistics is indicated for each electrode, as well its significance to multiple testing correction using a FDR procedure (‘*’ for significant; ‘ns’ for non-significant).