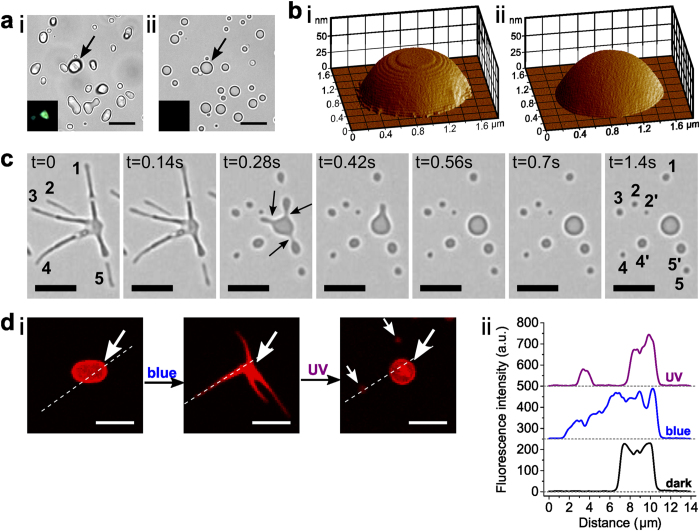
Figure 4.
(a) Optical microscopy images of trans-azoTAB:PAA microparticles (i) before and (ii) during UV-light irradiation to produce single spherical particles of cis-azoTAB:PAA; insets show particle highlighted by the arrow under polarized light indicating loss of birefringence after UV exposure; scale bars = 10 μm. (b) 3D AFM imaging of a single air-dried trans-azoTAB:PAA microparticle viewed (i) in the dark, and (ii) under in situ UV irradiation and transformation to cis-azoTAB:PAA, showing photo-induced loss of surface texture. (c) Time-lapse series of video images showing UV-induced fragmentation and division of a single trans/cis-azoTAB:PAA multipodal structure into a series of spherical particles of cis-azoTAB:PAA within 1 s. Arrows highlight localised pinching events; numbers correspond to spherical particles produced by fragmentation of marked filaments; scale bars = 5 μm. (d) (i) Confocal fluorescence microscopy images of a single azoTAB:PAA microparticle containing Cy5-ssDNA during blue/UV light-induced reconfiguration. Arrows highlight the position of the initial particle and products; scale bars = 5 μm. (ii) Corresponding fluorescence intensity profiles recorded along the dotted lines shown in (i).