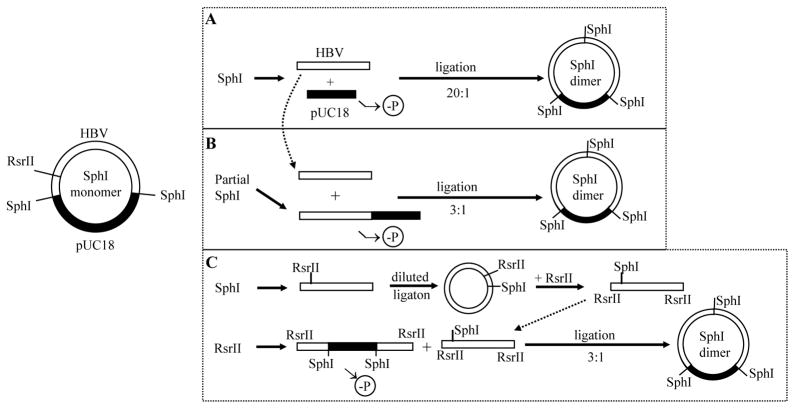
Fig. 1.
Strategies to convert an SphI monomer into an SphI dimer. pUC18 vector and HBV DNA are shown in black and white, respectively. In the established method (approach A), SphI-cut HBV DNA was ligated with SphI-cut, dephosphorylated pUC18 vector at high molar ratio. The efficiency of dimer formation is low due to the need for a three-way molecular ligation. In approaches B and C, ligation occurs between the 5.9-kb monomeric HBV DNA and pUC18 vector, through either the SphI site (approach B) or RsrII site (approach C). Such a two-way molecular ligation greatly enhances the efficiency of dimer formation.