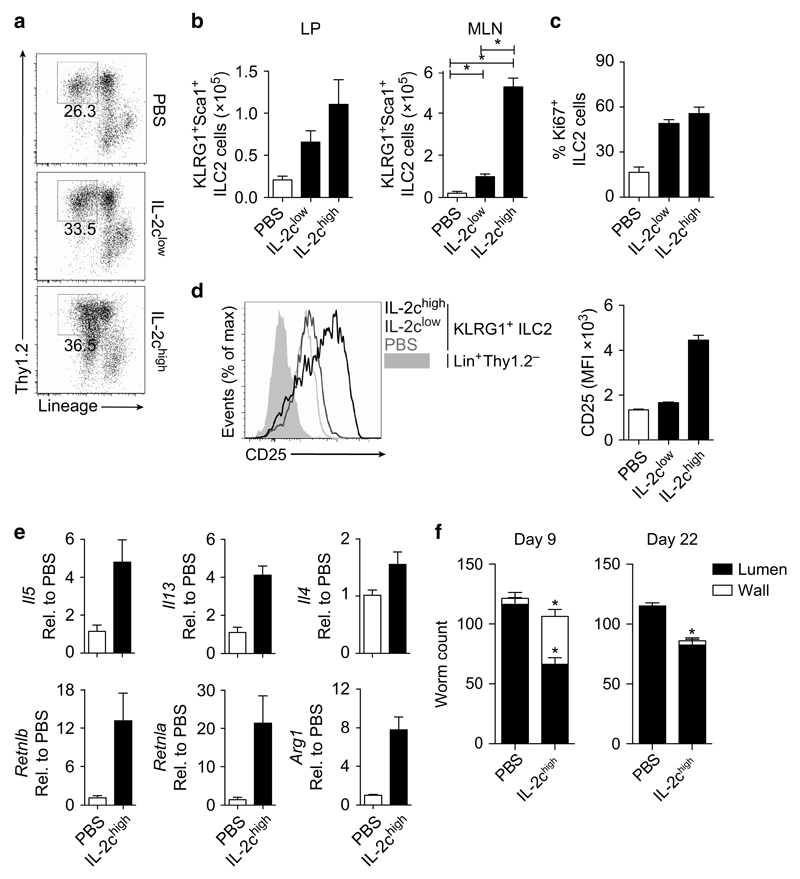
Figure 3.
Interleukin (IL-2)-expanded group-2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) can provide functional immunity to Heligmosomoides polygyrus infection. Rag2−/− were infected with 200 H. polygyrus larvae and treated with IL-2 complex (IL-2c) or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) as a control. Mice were harvested 5 days postinfection. (a) Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) plots of mesenteric lymph node (MLN) Lin−Thy1.2+ cells. (b) Total number of ILC2s (Lin−Thy1.2+ KLRG1+) in the lamina propria (LP) and MLN of treated mice. (c) Percentage of Ki-67+ ILC2s. (d) FACS plot and graphical representation of CD25 expression (mean fluorescence intensity (MFI)) on MLN ILC2s (Lin−Thy1.2+ KLRG1+) and Lin+ Thy1.2− nonlymphoid cells. (e) Gene expression of Il5, Il13, Il4, Retnla, Retnlb, and Arg1 in the small intestine (SI) of IL-2c-treated mice, expressed as fold change relative to PBS-treated mice. (f) Worm count of trapped larvae in the wall (white bars) and adult worms in the lumen (black bars) of IL-2c-treated mice at days 9 and 22 postinfection. Data are representative of three independent experiments with three to four mice per group. *P≤0.05 using the Mann–Whitney test.