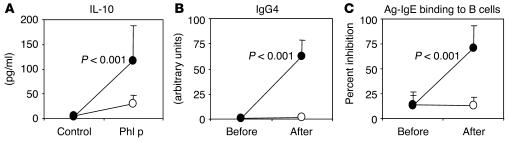
Figure 2.
Immunological changes after allergen immunotherapy. Following 2-year grass pollen immunotherapy (closed circles), there were significant increases in (A) allergen-stimulated PBMC production of IL-10 (78); (B) serum concentrations of grass pollen (Phleum P5) allergen-specific IgG4 (84); and (C) serum inhibitory activity for allergen-IgE binding to B cells (88) compared with controls (open circles). These changes were accompanied by a reduction in symptoms and rescue medication use during the pollen season (83); inhibition of the allergen (grass pollen) induced late cutaneous response.