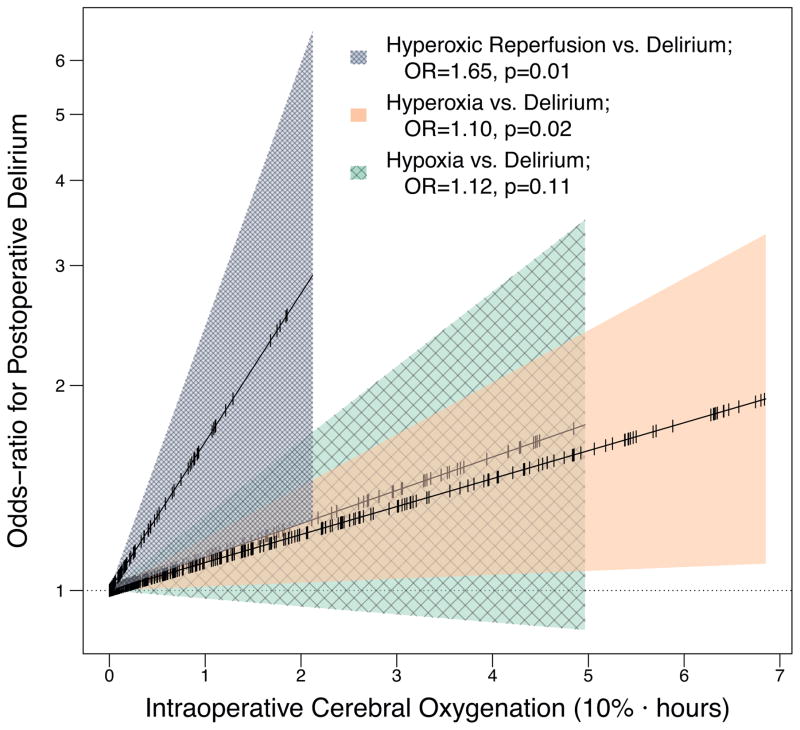
Figure 2. Associations between intraoperative cerebral hyperoxic reperfusion, cerebral hyperoxia, and cerebral hypoxia and postoperative delirium.
Odds ratios (OR) represent the odds of postoperative delirium for every 10%·hour (e.g., 20% above baseline for 30 minutes equals one 10%·hour hyperoxia) intraoperative oxygenation metric, adjusted for potential confounders, risk factors, and the other oxygenation metrics. For example, a patient with two 10%·hours of hyperoxic reperfusion had a 65% increase in the odds of delirium compared to the patient with one 10%·hours of hyperoxic reperfusion independent of the effects of hyperoxia prior to reperfusion, hypoxia, confounders, and risk factors on delirium. Cerebral oxygenation parameters (x-axis) were truncated at the 90th percentile to simplify exposition.