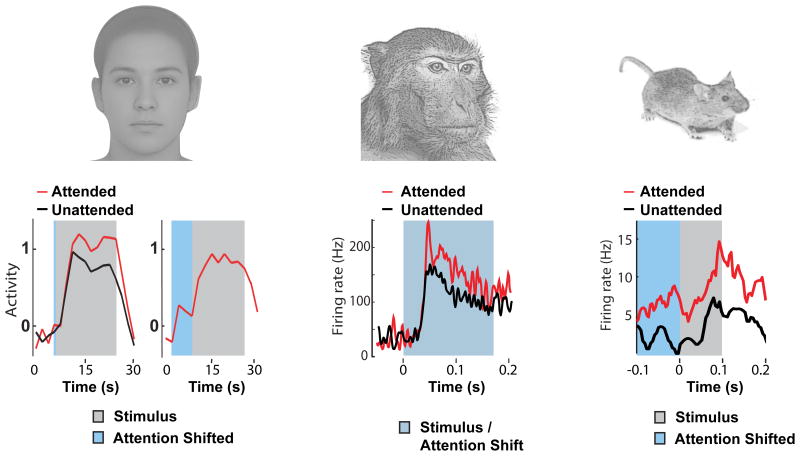
Figure 4. Thalamic gain control is evolutionarily conserved.
(A) Measurement of the BOLD response in human LGN during a visual attention task (28). Both evoked response (left panel, grey) and baseline activity in the absence of stimulus (right panel, blue) increase when attention is covertly directed to stimulus location. (B) Evoked responses of macaque LGN neurons were increases when attention was directed to the neuron's receptive field (29). (C) Attending to vision increases both baseline firing (blue portion) and evoked response (grey) of LGN neurons in mice performing a cross-modal attention task (27).