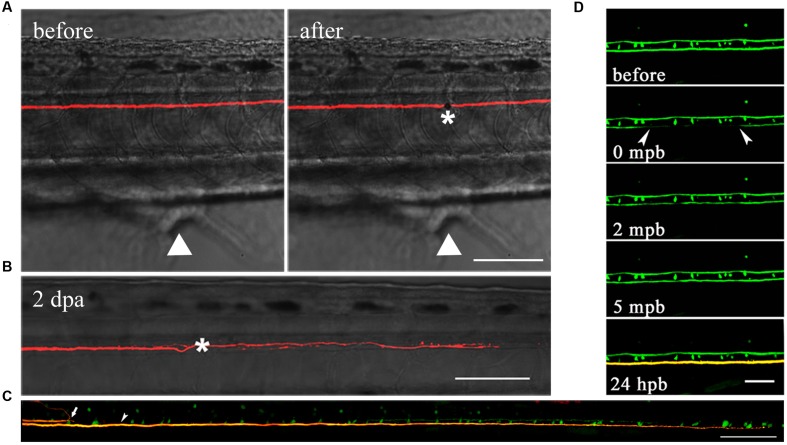
FIGURE 3.
M axons were completely severed by laser and have regenerative capacity after injury. (A) M axons were axotomized by two-photon laser before (left) and after (right). Asterisk, injury site; white arrowheads, cloacal pores. (B) Injured axons regenerated to hundreds of microns 2 days after axotomy. Asterisk, injury site. (C) Using transgenic Tg (Tol-056) lines, the uncut axon (bottom) was longer than the severed axon (top) which stopped at the lesion site, implying that laser-induced injured axons were physically disconnected. White arrow, severed axon; white arrowhead, uncut axon. (D) One-photon laser was used to photobleach axons. Green fluorescence recovered after several minutes. When the photobleached axon was labeled with red dye at 24 hpb, its structure was still physically connected. Scale bars: (A–C) 100 μm, (D) 50 μm.