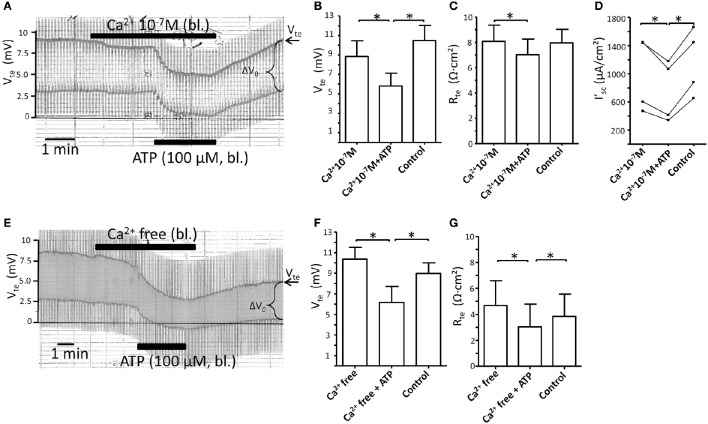
Figure 3.
Reduction or removal of extracellular Ca2+ does not affect the basolateral ATP-stimulated inhibition of NaCl absorption in isolated perfused mouse mTAL. (A) Representative original trace of the basolateral ATP effect in mouse mTAL during the reduction of basolateral extracellular Ca2+ to 100 nM. Recording of the electrical parameters Vte (transepithelial voltage) and ΔV0 (voltage deflection) in freshly dissected and perfused mouse mTAL used to quantify transport changes. Note the slight reduction of Vte and ΔV0 after reducing extracellular Ca2+ from 1.3 mM to 100 nM. (B–D) Summary of the transepithelial voltages (Vte), the transepithelial resistances (Rte) and the calculated equivalent short-circuit current (I'sc) before, during (after 1 min) and after ATP wash-out (2 min after). (n = 4, *p < 0.05 by student's T-test). (E) Representative original trace of the basolateral ATP effect in mouse mTAL during the removal of basolateral extracellular Ca2+ (5 mM EGTA). Note the continuous reduction of Vte and ΔV0 after removing extracellular Ca2+. (F,G) Summary of the Vte and Rte before, during (after 1 min) and after ATP wash-out (2 min after). (n = 4, *p < 0.05 by student's T-test). Note the artificially low Rte values in (G), especially during application of bl. ATP.