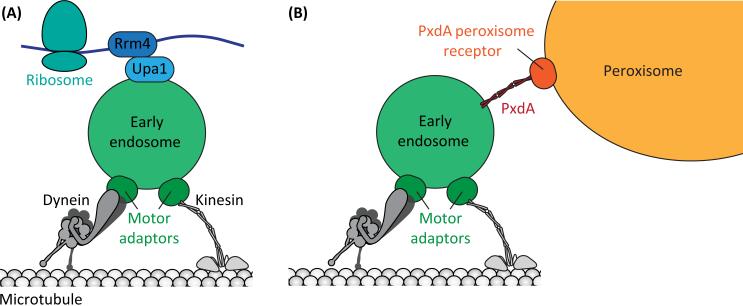
Figure 1. Mechanisms of Cargo Hitchhiking.
(A) In U. maydis ribosome-associated mRNAs hitchhike on EEs. The RNA-binding protein (RBP) Rrm4 links the mRNA to the early endosome-binding protein, Upa1. Kinesin-3 and dynein/dynactin motors are recruited via the motor adaptor Hok1 (related to mammalian Hook3). (B) In both U. maydis and A. nidulans peroxisomes hitchhike on EEs. The endosome-interacting protein, PxdA, is required for peroxisome hitchhiking and may act as a tether between the two organelles. The putative peroxisome receptor for PxdA has not yet been identified. Kinesin-3 and dynein/dynactin motors are recruited via the motor adaptor Hok1/HookA. Although not depicted here, Hook associates with endosomes via a larger protein complex that contains the homologs of the fused toes (FTS) and fused toes and hook interacting protein (FHIP) proteins.