Figure 5. Neddylation inhibition decreases liver inflammation and reduces Kupffer cell activation.
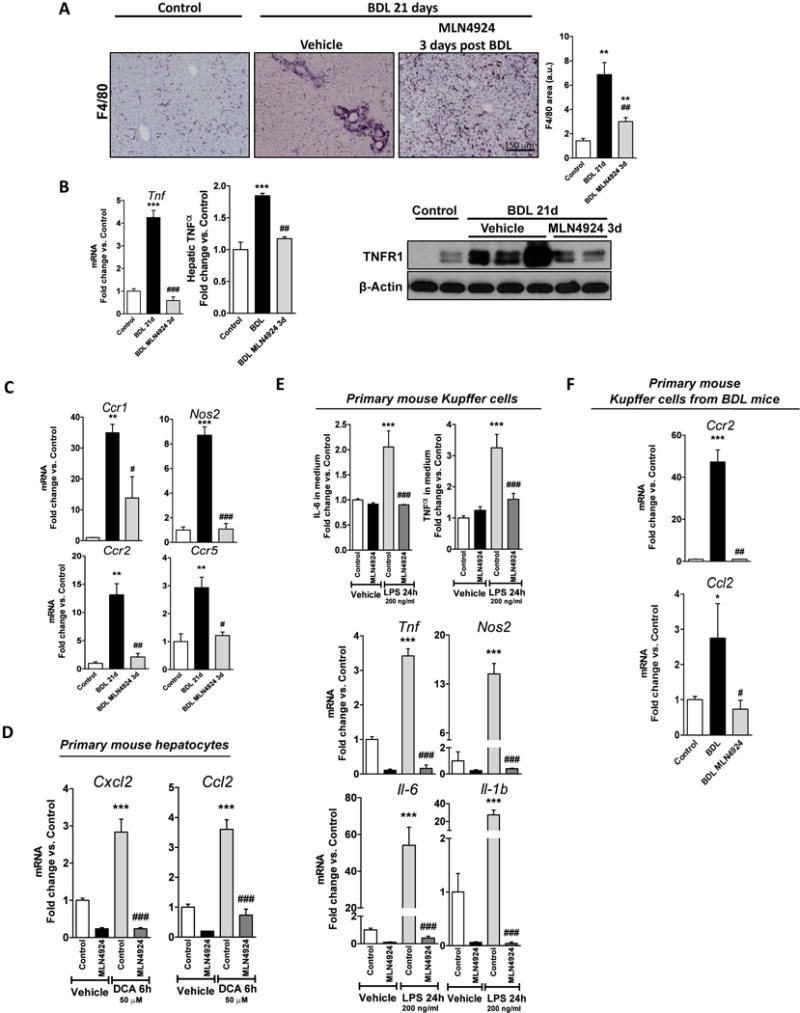
(A) F4/80 staining; (B) Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) and TNFα receptor (TNFR1) expression; and (C) mRNA levels of inflammatory markers in mouse livers. (D) mRNA levels of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 (Cxcl2) and chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (Ccl2) in mouse primary hepatocytes exposed to 50 μM deoxycholate bile acid (DCA) for 6 hours and treated with 3 μM MLN4924 or vehicle. (E) Interleukin-6 and TNFα levels in the extracellular media (top) and mRNA levels of inflammatory markers (bottom) of lipopolyssacharide (LPS)-stimulated (200 ng/ml, 24 hours) Kupffer cells (KC) treated with 3 μM MLN4924 or vehicle. (F) Ccr2 and Ccl2 mRNA levels in in vivo activated primary KC after MLN4924-treatement. Control (n=5), 21 days BDL (n=10) and MLN4924 [treated 3 days after surgery (n=5)]. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 vs. control and #p<0.05 MLN4924 treated vs. BDL treatment are indicated. At least triplicates were used for each in vitro experimental condition.
