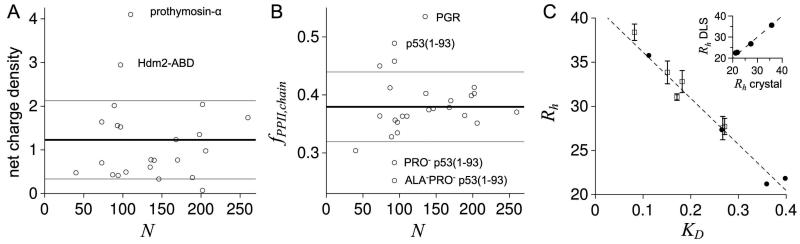
Figure 2.
A) Net charge density calculated from sequence for each dataset IDP. B) Chain-averaged PPII propensity calculated from sequence for each dataset IDP using experimental propensities.79 In A and B, bold lines are dataset averages, whereas grey lines are averages ± the standard deviation. C) Rh (in Å) and KD for the IDPs identified in panels A and B and the folded proteins chicken egg albumin, bovine erythrocyte carbonic anhydrase, Staphylococcal nuclease, and horse heart myoglobin. Open squares are DLS-measured Rh, from largest to smallest, for the IDPs PGR (38.4 ± 0.9Å), prothymosin-α (33.8 ± 1.3Å), p53(1-93) (32.8 ± 1.2Å), Hdm2-ABD (31.0 ± 0.5Å), ALA−PRO− p53(1-93) (27.7 ± 0.9Å), and PRO− p53(1-93) (27.5 ± 1.3Å). Filled circles are Rh estimated as one-half the maximum Cα-Cα distance in the crystallographic structures of albumin,81 carbonic anhydrase,82 nuclease,83 and myoglobin.84 KD is the distribution coefficient determined by SEC. Standard deviations from measuring KD were < 0.007. The dashed line is a linear fit of Rh to KD applied to the filled circles (folded proteins), which was used to estimate Rh from KD for the IDPs. Table S1 lists the averages of the DLS-measured and KD-estimated Rh for each of the 6 IDPs. Inset: Filled circles are Rh measured by DLS for the folded proteins compared to Rh estimated from crystal structures as one-half the maximum Cα-Cα distance, showing good agreement. DLS-measured Rh for each folded protein was: albumin (35.6 ± 0.5Å), carbonic anhydrase (26.8 ± 0.8Å), myoglobin (22.7 ± 0.8Å), and nuclease (22.4 ± 0.4Å).