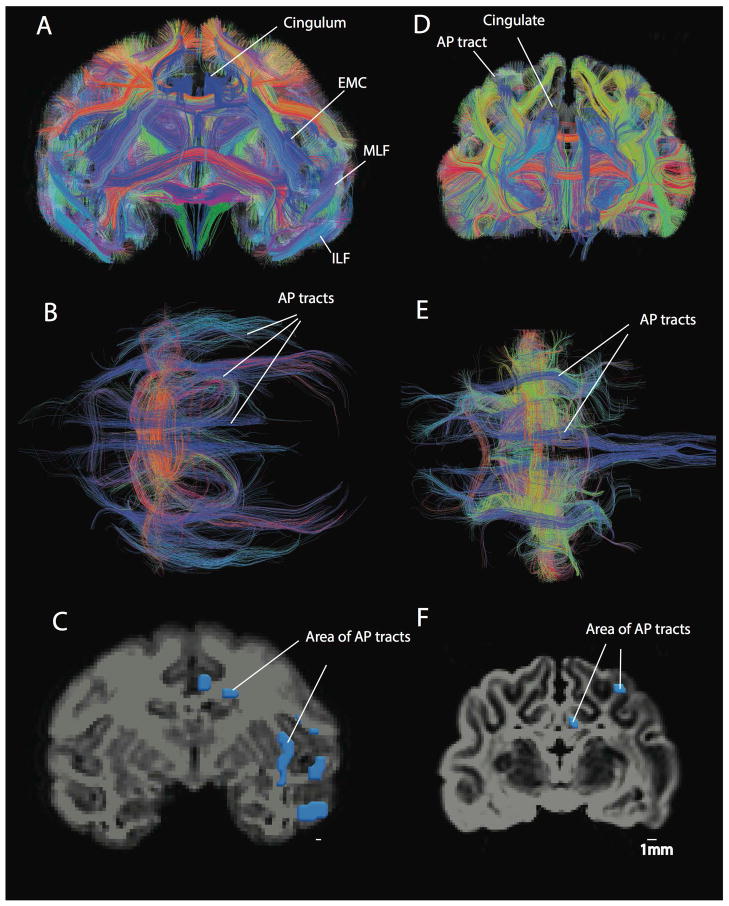
Figure 5.
Anterior-posterior corticocortical tracts in a macaque (A–C) and a cat (D–F). A number of anterior-posterior corticocortical tracts such as the inferior longitudinal fasciculus (ILF), the middle longitudinal fasciculus (MLF), the extreme capsule fibers (EMC) as well as the cingulum are observed within the white matter of the macaque isocortex. This is evident from coronal (A) and axial views (B). In contrast, a coronal (D) and an axial view (E) show that the cat possesses very few anterior-posterior cortical tracts. Regions of interest were used to measure the area of anterior-posterior corticocortical tracts in the macaque (C) and cat (F). The area of anterior-posterior cortical tracts was measured in a coronal section anterior/rostral to or at the level of the lateral geniculate nucleus. Anterior-posterior tracts are in blue. Tracts coursing lateral to medial are in red and tracts coursing across the dorsal-ventral axis are in yellow. Scale bar: 1mm.