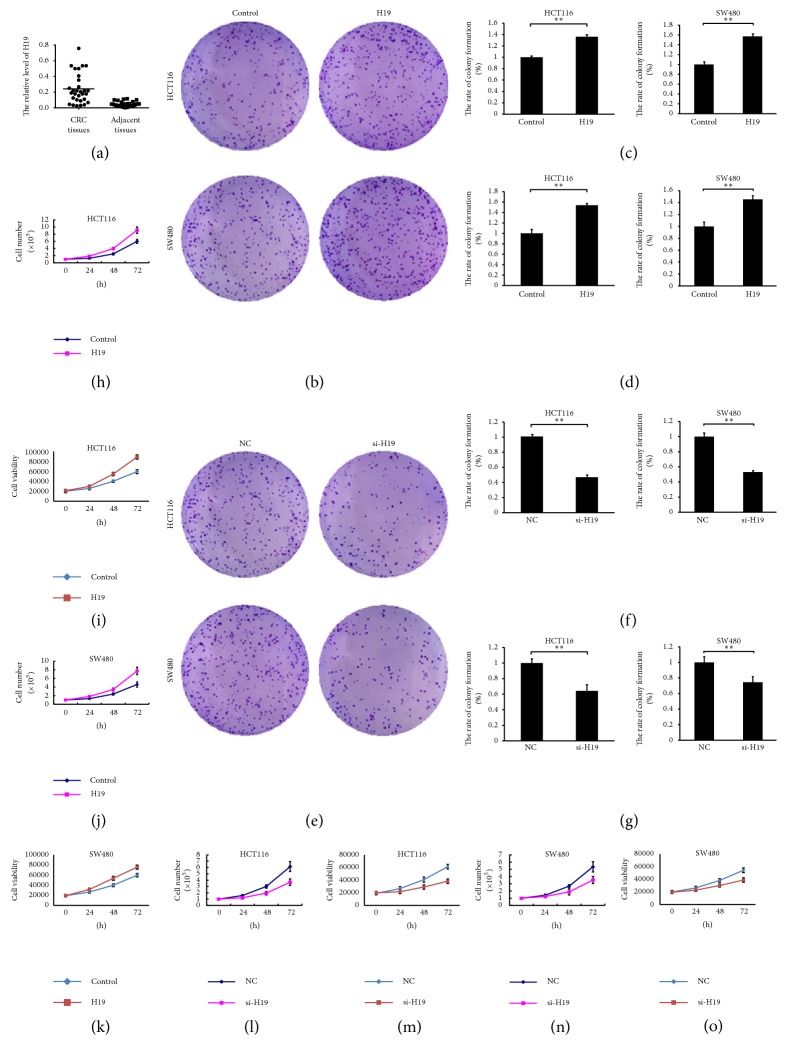
Figure 1.
H19 is highly expressed in CRC tissues and promotes cell proliferation. (a) H19 expression is significantly increased in CRC tissues compared with adjacent normal tissues, as demonstrated by RT-PCR. ((b) and (c)) H19 overexpression increases the colony formation rate of HCT116 and SW480 cells (soft-agar assay, P < 0.01). (d) H19 overexpression increases the colony formation rate of HCT116 and SW480 cells (plate colony formation assays, P < 0.01). ((e) and (f)) H19 knockdown decreases the colony formation rate of HCT116 and SW480 cells (soft-agar assay, P < 0.01). (g) H19 knockdown decreases the colony formation rate of HCT116 and SW480 cells (plate colony formation assays, P < 0.01). ((h) and (i)) H19 overexpression promotes HCT116 cell proliferation (cell growth curve and cell viability assay, P < 0.05). ((j) and (k)) H19 overexpression promotes SW480 cell proliferation (cell growth curve and cell viability assay, P < 0.05). ((l) and (m)) H19 knockdown inhibits HCT116 cell proliferation (cell growth curve and cell viability assay, P < 0.05). ((n) and (o)) H19 knockdown inhibits SW480 cell proliferation (cell growth curve and cell viability assay, P < 0.05). “∗∗” refers to P < 0.01.