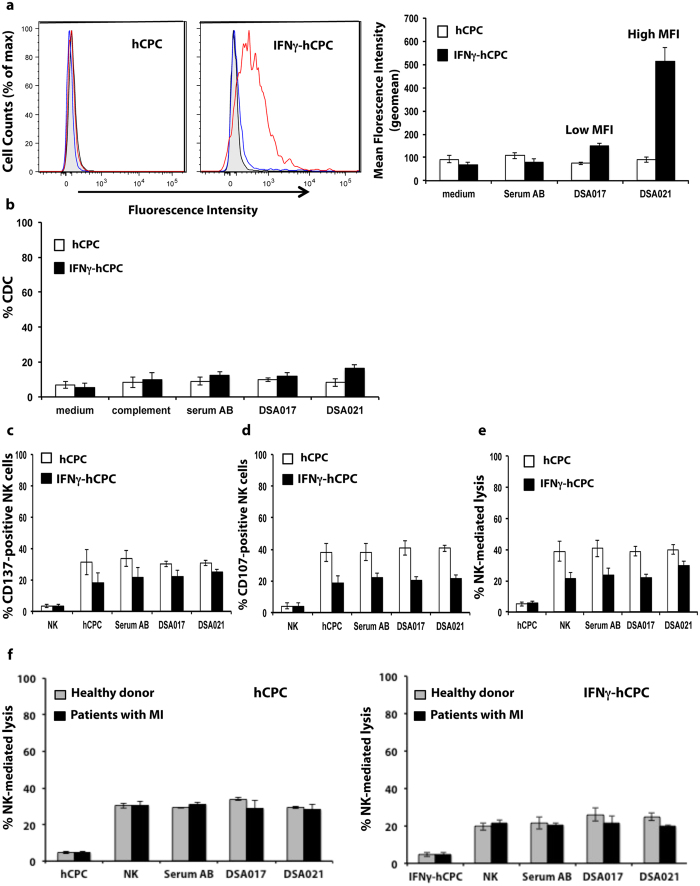
Figure 7. DSA-HLA-II do not induce antibody-mediated cytotoxicity.
DSA-HLA-II-DR4 sera (n = 2) were incubated with HLA-DR4-positive hCPC or IFNγ-hCPC (n = 2) then their reactivity was determined as MFI by flow cytometry. (a) Left panel showing representative histograms of DSA017 (blue) and DSA021 (red) interactions against control serum AB (black) and medium alone (filled gray). Mean MFI (geomean) values ± SD from three different experiments of each hCPC compared to serum AB and medium controls (right panel). (b) HLA-DR4-positive hCPC or IFNγ-hCPC (n = 2) were cultured alone, with control serum AB, or with DSA-HLA-II-DR4 sera (DSA017, 021), in the presence or absence of complement, then their capacity to induce CDC was evaluated as % 7AAD-positive hCPC. Results are presented as mean values ± SD from four different experiments of each hCPC. (c–e) IL-15-activated NK cells were cultured alone or with HLA-DR4-positive hCPC or IFNγ-hCPC (n = 2) in the presence of control serum AB or DSA-HLA-II-DR4 sera. (c) % CD137-positive NK cells, (d) % CD107-positive NK cells and (e) % NK-mediated lysis evaluated as % 7AAD-positive hCPC. Results represent mean values ± SD from three different experiments of each hCPC. (f) % Healthy- or patient-NK-mediated lysis evaluated as % 7AAD-positive hCPC. Results represent mean values ± SD from three different experiments. Statistical analyses were performed using Mann–Whitney test for non-paired groups and were non-significant.