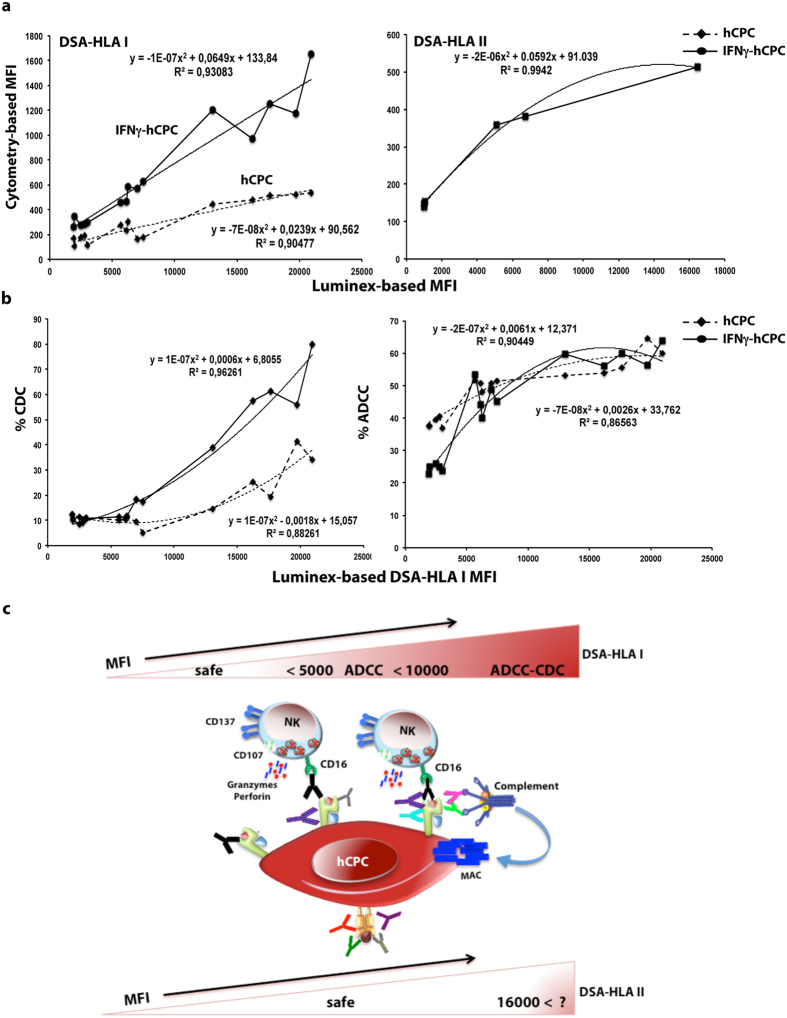
Figure 8. Translational dimension of DSA-HLA sensitization in the context of hCPC therapy.
(a) Left panel DSA-HLA-I (n = 15) and right panel DSA-HLA-II (n = 6) sera flow cytometry-detected MFIs values were plotted as function of their Luminex-detected MFIs. (b) Left panel % CDC and right panel % ADCC against hCPC or IFNγ-hCPC plotted as function of their Luminex-detected MFIs. Correlations curves along with their respective R2 values are indicated. (c) Schematic representation of DSA-HLA-sensitization risk for hCPC-based therapy. DSA-HLA-I of Luminex-detected high mean florescence intensity (MFI) present an absolute risk of humoral rejection inducing both CDC and ADCC through complement activation and the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC) or by bridging NK cells CD16 receptor with HLA-I molecules at the surface of hCPC, respectively. DSA-HLA-I with Luminex-detected MFIs ranging from 5000 to 10000 present a relative risk of humoral rejection bridging NK cells CD16 receptor with HLA-I molecules at the surface of hCPC will induce only ADCC. DSA-HLA-I having Luminex-detected MFIs < 5000 and DSA-HLA-II with MFI up to 16000 are safe.