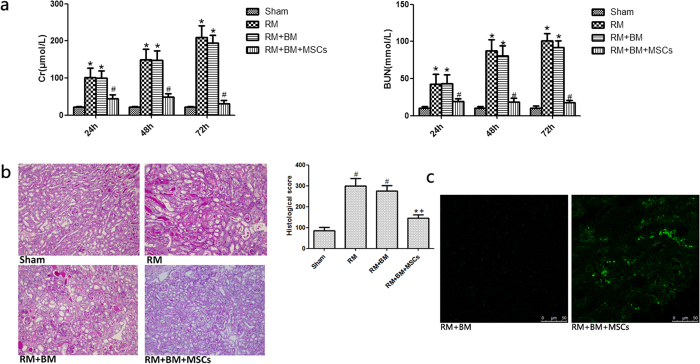
Figure 1. Biological membrane packing of Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) on the renal tissue ameliorate rhabdomyolysis (RM)-induced acute kidney injury (AKI).
(a) Compared with sham mice, biological membrane packing of Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) on the renal tissue significantly reduced serum creatinine (SCr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels 24, 48 and 72 hours after RM. *p < 0.05 versus the sham group; #p < 0.05 versus the RM and RM + BM group (n = 6). (b) Periodic acid-Schiff-stained sections of mouse kidneys (200×). Sham: Normal kidney section. RM(rhabdomyolysis): Kidney section of glycerol-treated mouse showing tubular necrosis and cast formation. RM + BM: Kidney section of glycerol-treated mouse and biological membrane(BM)-wrapped kidney also showing tubular necrosis and cast formation. RM + BM + MSCs: Kidney section of biological membrane-packed mesenchymal stem cells(MSCs) on the renal tissue and glycerol-treated mouse showing morphological damage significantly improved. Note: *p < 0.05 versus the RM group; †p < 0.05 versus the RM + BM group; #p < 0.05 versus the sham group (n = 8). (c) Images of the transplanting MSCs-GFP under biological membrane. MSCs-GFP survived on the surface of renal parenchyma. GFP-labelled MSCs (green) were detected using two-photon fluorescence confocal microscopy.