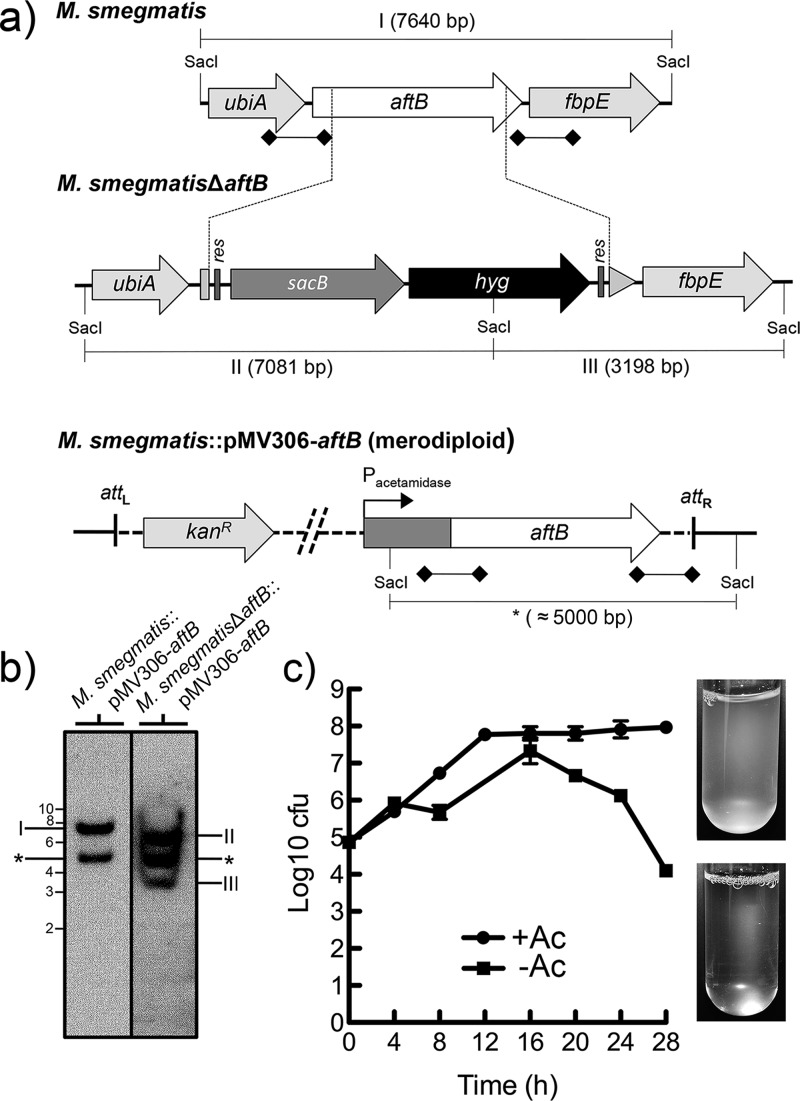
Figure 2.
Generation of a conditional aftB mutant in M. smegmatis. (a) A map of the aftB region in the parental M. smegmatis strain, its corresponding region in the conditional M. smegmatisΔaftB::pMV306-aftB mutant and merodiploid strain; res, resolvase site; hyg, hygromycin resistance gene from Streptomyces hygroscopicus; sacB, sucrose counter-selectable gene from Bacillus subtilis. Digoxigenin-labeled probes were derived from ∼1 kb upstream and downstream flanking sequences that were used to construct the knockout plasmid and are indicated by thick lines with square ends. SacI-digested bands expected in a Southern blot are indicated in I, II, III, and *. (b) The Southern blot of SacI-digested genomic DNA from the merodiploid and conditional aftB mutant with expected bands I, II, and III. The asterisk (*) indicates a band appearing as a result of a second aftB copy integration into mycobacterial chromosome. Representative lanes are from the same Southern blot and are grouped next to each other for clarity. (c) Log CFU obtained from cultures of M. smegmatisΔaftB pMV306-aftB grown with and without acetamide (Ac). Log10 CFU values were calculated from different dilutions at different time points from a single experiment. The images on the right show cultures after 28 h of growth in the presence and absence of Ac. Results are mean ± SD from n = 3 colonies per strain and are from one representative of two independent experiments.