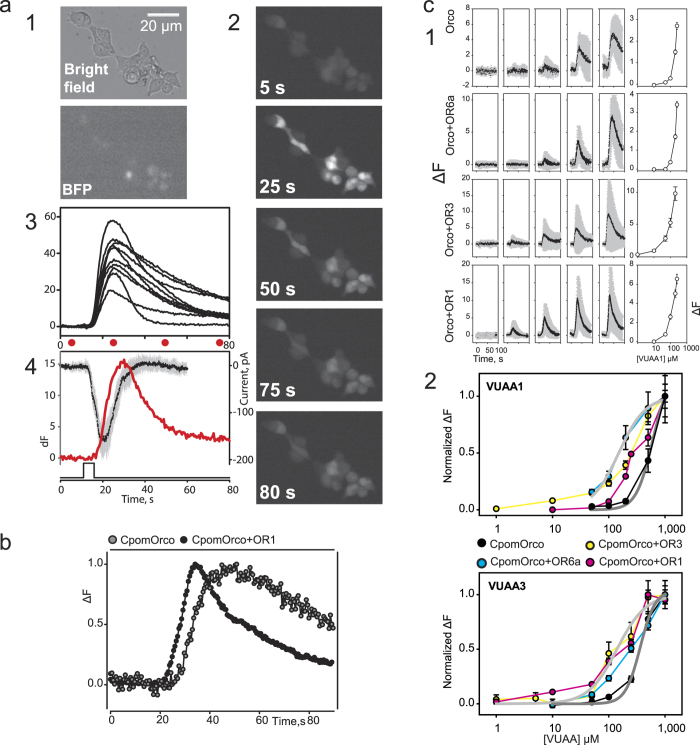
Figure 2. Electrophysiology and pharmacology of CpomORs expressed in HEK293T cells.
(a) Activation of HEK293T cells expressing CpomOrco by VUAA1. CpomOrco was co-expressed with BFP (mostly localized in nuclei) for parallel expression control (a1); HEK293T cells were stimulated with VUAA1 (250 μM, a2). The agonist stimulation elicits Ca++i increase in the cells (a2, a3). Each image (a2) was acquired at the times indicated on panels and by red circles under calcium signal curves (intensity of fluorescent curves, a3). Note: the BFP negative cells (compare bright field image with BFP and a2) did not generate appreciable calcium signal. (a4) Activation of ion channels underlies the generation of the agonist dependent calcium signal. Whole-cell voltage clamp recording was obtained from the cell that generated calcium signal in response to VUAAs (250 μM). VUAA1 activated inward current (black line, average of three responses, grey bars - SD) that kinetically preceded calcium signal (red line) and thus may underlie agonist dependent calcium influx. Holding potential was −50 mV. Time scale and diagram of stimulus application shown in a4 is common for a3 and a4. (b) The kinetics of calcium responses mediated by the activity of the homomeric Orco or Orco + OR complexes were different. Cells transfected with CpomOrco + OR1 could be characterized by faster activation/deactivation kinetics (black circles and line). Calcium response traces represent average of normalized responses of many cells recorded from the same preparation. (c) VUAA1 stimulation elicits dose-dependent Ca++i increase in HEK293T cells expressing either homomeric Orco or Orco + OR complexes (plot series are labelled respectively). (c1) Data within each row were obtained from single preparation; right panels, the respective concentration dependences. Note: the maximal agonist concentration used in these experiments (VUAA1 250 μM) is likely not a saturating concentration. (c2) Concentration dependences of VUAA1 and VUAA3. Data were obtained in the separate series of experiments. The response amplitudes were used to generate the agonist concentration dependences. The average peak amplitudes of the responses of different cells (n = 57–216) were normalized to the maximal responses usually elicited by application of a saturating concentration (1000 μM) of VUAA1 or VUAA3. Note: homomeric CpomOrco (dark grey curves) is less sensitive to the agonists ([VUAA1]1/2 ~ 520 μM, [VUAA3]1/2 ~ 362 μM) than the heteromeric complexes (e.g. light grey curves, [VUAA1]1/2 ~ 150 μM, [VUAA3]1/2 ~ 140 μM).