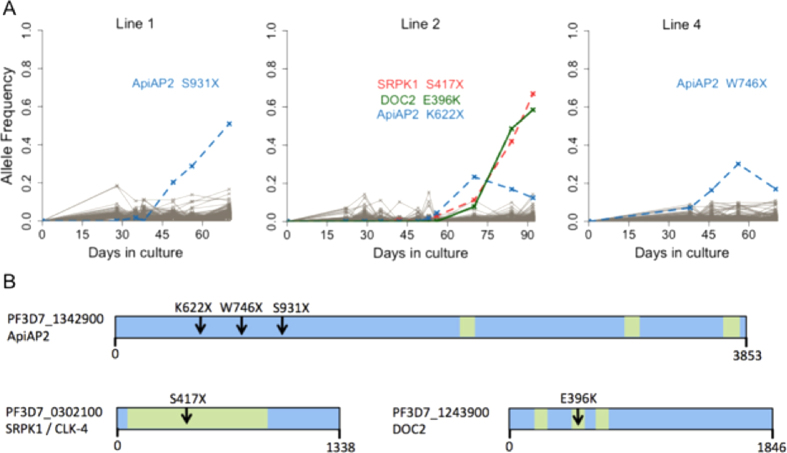
Figure 2. Selection of novel SNP alleles during culture adaptation of three unrelated P. falciparum clinical isolates in The Gambia.
(A) Allele frequencies at each sampled time point were determined by alternative sequence read counts for each SNP, and novel alleles reaching a frequency of more than 20% over the time course are plotted in colour (dashed lines indicate nonsense mutant alleles). The temporal frequency changes for these five SNPs attained genome wide significance (P < 10−9 for each; read counts at each timepoint are given in Table S2). (B) Gene models with an arrow indicating the mutation position for each emerging SNP identified in panel A. Green boxes indicate predicted functional domains in each gene: AP2 domains in an ApiAP2 transcription factor gene, the catalytic domain in the serine/threonine protein kinase gene SRPK1, and Calcium/lipid-binding C2 domains in DOC2. The numbers of codons in each gene are indicated underneath each scheme.