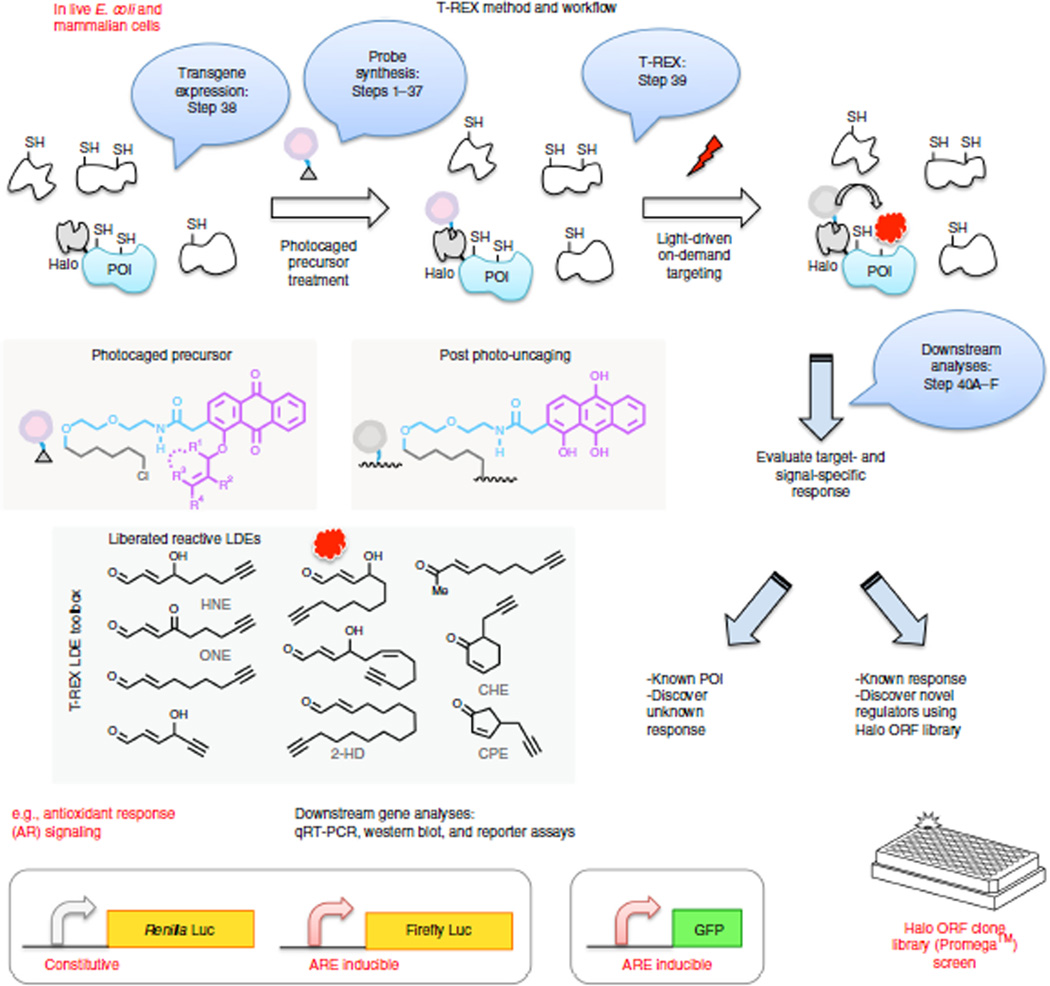
Figure 2.
On-target, on-demand redox signaling enabled by T-REX. Bubbles indicate experimental steps described in the protocol. Either E. coli or mammalian cells expressing HaloTag-fused proteins of interest (POIs) are treated with designated photocaged precursors (5–25 µM, 2 h) to achieve a 1:1 covalent binding between the HaloTag and the photocaged probe. After rinsing cycles, exposure of the cells (for 3–20 min) to low-energy light (0.3 mW/cm2, 365 nm) at room temperature elicits rapid liberation of a reactive signal (lipid-derived electrophiles (LDEs), inset) from the photocaged probe bound to HaloTag. Proximity enhancement62 facilitates on-target, on-demand covalent modification of amino acid residue(s) on the POIs, typically cysteines. HNE is also known to be capable of modifying lysine and histidine (see text). Regardless of residue specificity, T-REX is able to ping one potential responsive protein with a precision dose of reactive lipid. Irrespective of residue identity, in-gel fluorescence analysis reports on the presence of HNE modification on the POIs. Residue specificity in POI modification is determined by LC–MS/MS analysis post cell lysis and resin-assisted enrichment (Fig. 5c). Once a specific sensor protein has been earmarked by T-REX, target- and residue(s)-specific post-translational modification can be directly linked to the signaling function of interest in an otherwise unperturbed cellular background. T-REX can (i) interrogate specific redox-linked signaling responses and (ii) discover novel regulators that upon selective lipidation are sufficient to elicit a biologically relevant response. Generality and scope in terms of both target and signal specificity are exemplified with distinct vertebrate sensor proteins (e.g., Keap1, RRM1, HSPB7) and structurally distinct LDEs (inset). Pathway activation is analyzed using dual-luciferase reporter assays or GFP reporter assays by flow cytometry. Endogenous downstream gene activation can be analyzed by qRT-PCR and western blotting.