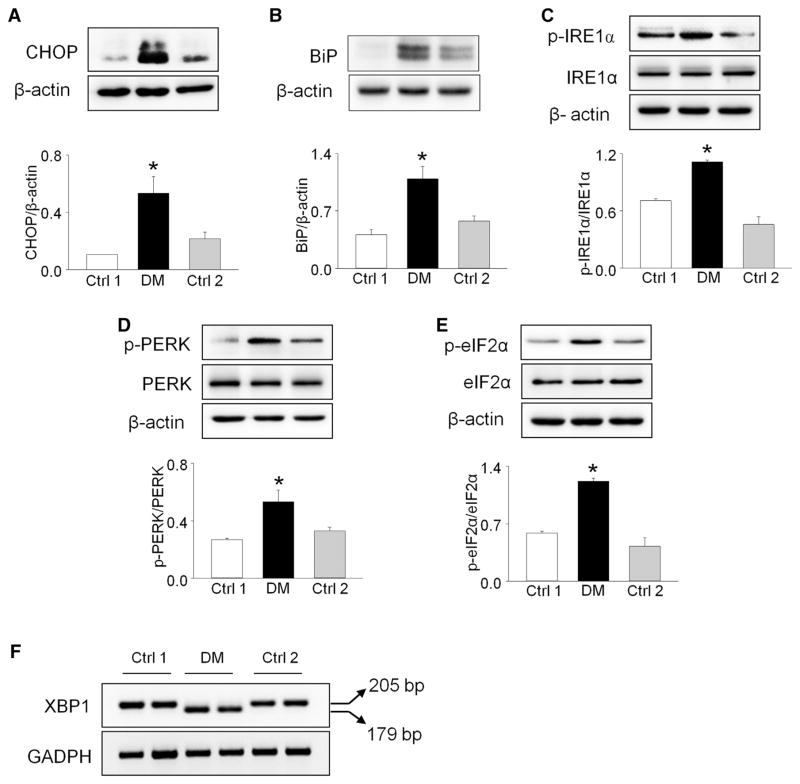
FIGURE 2. Maternal type 2 diabetes mellitus triggers endoplasmic reticulum stress in developing heart.
A to E, Protein levels of phosphorylated protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase, protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase, p-IRE1α, IRE1α, p-eIF2α, eIF2α, C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), and binding immunoglobulin protein (BiP) were determined in E12.5 embryonic hearts. F, XBP1 messenger RNA splicing in E12.5 embryonic hearts. Arrows point to actual size of bands. Experiments were performed using 3 embryonic hearts from 3 different dams per group. *Significant differences (P < .05) compared with other groups.
Ctrl 1, control group fed normal diet; Ctrl 2, control group fed 60% high-fat diet during pregnancy; DM, group fed high-fat diet.
Wu et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus induces congenital heart defects. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2016.