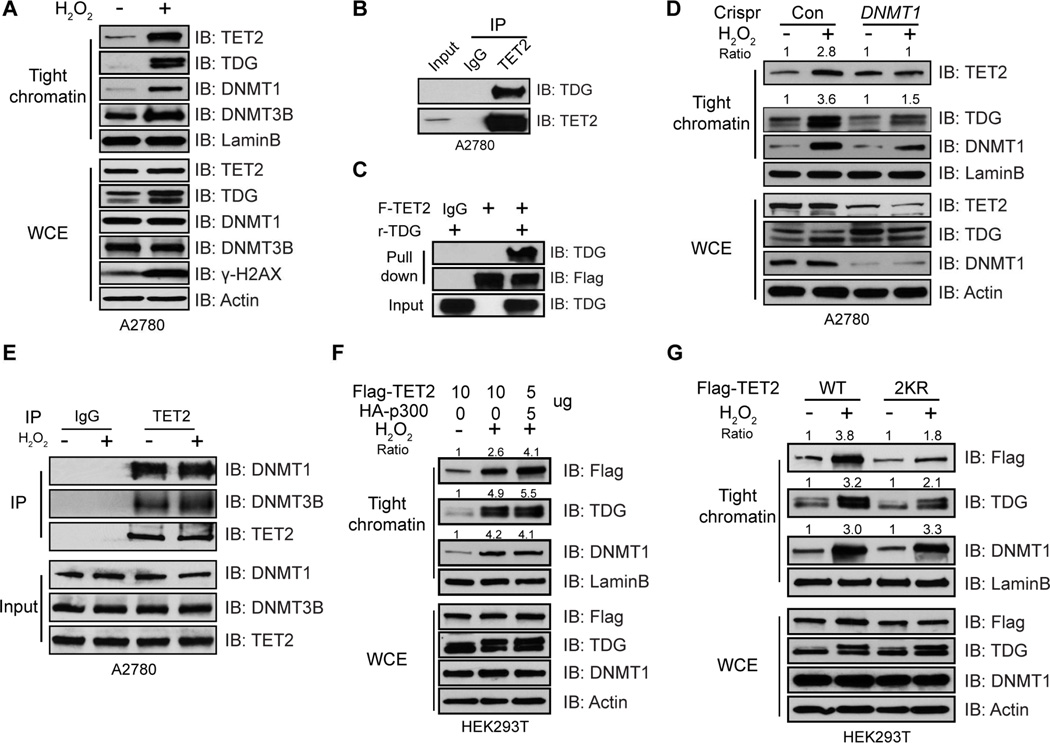
Figure 6. Acetylation enhances targeting of TET2 to chromatin during OS.
(A) A2780 cells treated with or without H2O2 for 30 min were extracted sequentially with various buffers. Proteins resistant to 0.45M NaCl buffer are considered as tight chromatin fraction and analyzed by IB. Tight chromatin DNMT3B is referred to DNMT3B that is resistant to 2 M NaCl buffer. WCE was used as input.
(B) Endogenous TET2 complexes were IPed from A2780 nuclear extract and analyzed by IB.
(C) Immunoprecipitated TET2 bound on beads was incubated with or without 500 ng recombinant TDG overnight. Bound proteins were analyzed by IB. IgG was used as negative control.
(D) A2780 Con and DNMT1 knockdown cells were treated with or without H2O2 for 30 min. Tight chromatin and WCE were analyzed by IB. Band intensities were quantified by ImageJ and normalized to LaminB loading control.
(E) Endogenous TET2 complexes were IPed from A2780 cells treated with or without H2O2 for 30 min and analyzed by IB. Spermine and Spermidine were added to extract proteins bound to chromatin.
(F and G) HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-TET2, in the presence or absence of HA-p300 (F), or TET2 WT, or 2KR mutant (G) for 2 days and treated with or without H2O2 for 30 min. Tight chromatin proteins and WCE were analyzed by IB. Band intensities were quantified by ImageJ and normalized to LaminB loading control. A pre-determined ratio between TET2 and p300 constructs was used in (F) to achieve equal levels of total TET2 proteins.
See also Figure S6.