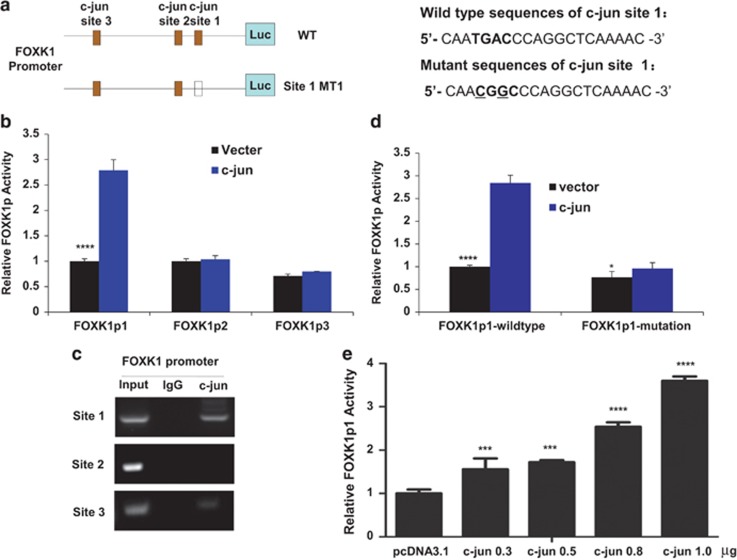
Figure 3.
C-jun upregulates FOXK1 expression by directly binding to the proximal promoter of the FOXK1 gene. (a) Schematic representation of the promoter region of FOXK1 (FOXK1p). The luciferase reporter constructs (FOXK1p1, FOXK1p2 and FOXK1p3) contained the FOXK1 promoter with three potential c-jun binding sites upstream of a luciferase gene. WT: wild type; MT: mutated. (b) The reporter constructs used in c-jun transfection experiments. C-jun activates the FOXK1 promoter after co-transfection in MKN28 cells. Luciferase activity was measured 48 h after transfection. Luciferase activity is expressed as the ratio of promoter reporter activity to control vector luciferase activity. ****P<0.0001. (c) ChIP was performed using an anti-c-jun antibody or control immunoglobulin G (IgG). The FOXK1 promoter region to which c-jun bound was significantly enriched after immunoprecipitation with an anti-c-jun antibody. (d) Primer sequences used to generate site-directed mutations. The FOXK1p1 (wild type 1) location was labeled in bold and mutated nucleotides are underlined. Site-directed mutagenesis of FOXK1p1 was performed to generate FOXK1p1-MT. ****P<0.0001; *P>0.05. (e) The c-jun protein stimulated FOXK1p1 activity, and the relative luciferase activity was enhanced by c-jun in a dose-dependent manner. ***P<0.001; ****P<0.0001