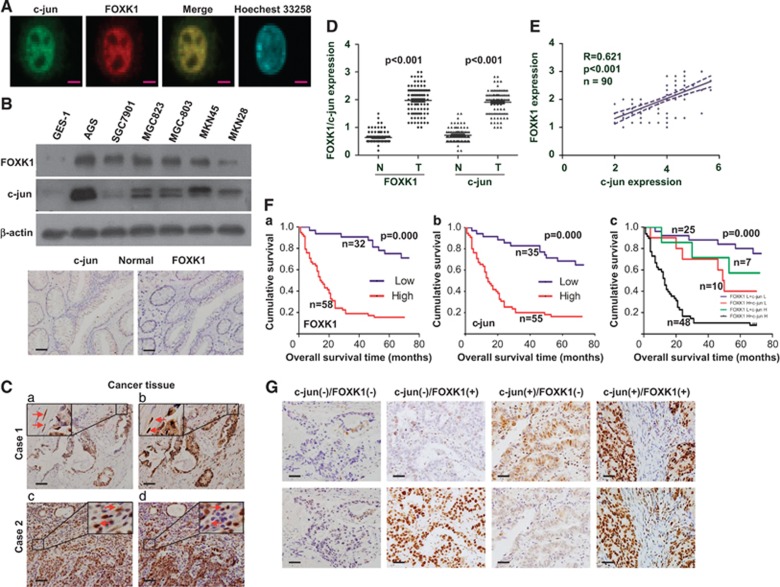
Figure 4.
Positive correlation between c-jun and FOXK1 expression in GC. (A) Double staining of FOXK1 and c-jun in MKN28 cells in an indirect immunofluorescence assay; the nuclei were counterstained using Hoechst 33258. (B) FOXK1 and c-jun expression levels were detected in GC cell lines and in the immortalized normal gastric epithelial cell line GES-1 using western blot analysis. (C) C-jun (a and c) and FOXK1 (b and d) expression levels in normal or cancerous gastric tissue specimens were detected using immunohistochemical (IHC) assays. Normal mouse IgG was used as the isotype control for the first antibody (a and b). (D) The average scores of the two proteins in normal and cancerous GC tissues. P<0.001 between normal and cancer tissues. (E) FOXK1 and c-jun-positive staining was quantified, and the correlation between these proteins was analyzed using the Spearman's correlation method. P<0.001. (F) Kaplan–Meier overall survival analysis of GC patients. Survival analysis was performed according to the expression status of FOXK1 (a) and c-jun (b), as well as the combined expression status of FOXK1 and c-jun (c). (G) Representative IHC images for tissues are shown. Scale bars represent 20 μm in (A) and 100 μm in (C and G)