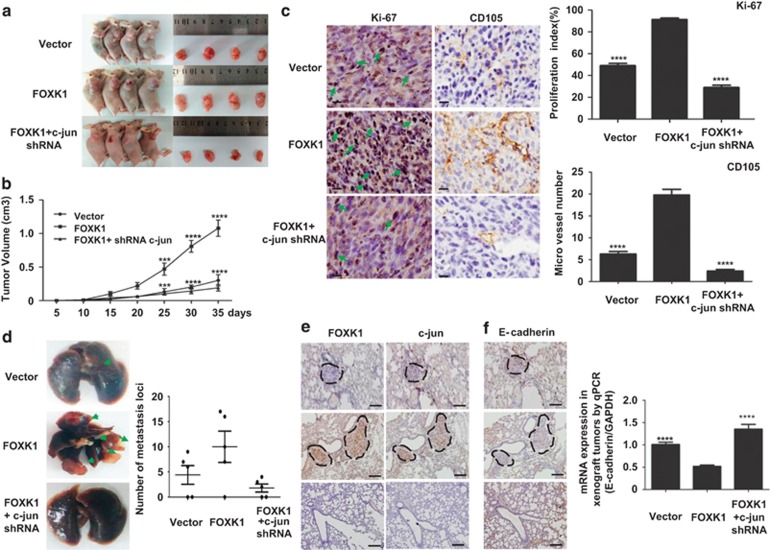
Figure 7.
C-jun facilitates FOXK1-mediated cell proliferation, EMT and liver metastasis in GC in vivo. (a) Evaluation of tumorigenesis in nude mice that were subcutaneously injected with MKN28-vector, MKN28-FOXK1 and MKN28-FOXK1-c-jun short hairpin RNA (shRNA) cells. The images were captured on day 35 after injection. (b) Tumor size was measured weekly after tumor cell inoculation in each group. ***P<0.001; ****P<0.0001; vector versus FOXK1 and FOXK1 versus FOXK1-c-jun shRNA, respectively. (c) C-jun knockdown significantly inhibited FOXK1-induced proliferation (Ki-67, ****P<0.0001, vector versus FOXK1 and FOXK1 versus FOXK1-c-jun shRNA, respectively), and a considerable decrease of tumor vessel density (CD105, ****P<0.0001, vector versus FOXK1 and FOXK1 versus FOXK1-c-jun shRNA) was observed using immunohistochemisty (IHC). (d) Mice were orthotopically transplanted with MKN28 cells (n=3 in each group). Representative images of metastatic loci in the lungs are shown. The number of metastatic loci in the lung was counted (right). (e) Confirmation of FOXK1 and c-jun expression by IHC staining. (f) The expression of E-cadherin in tumors derived from MKN28 cells was determined using IHC staining quantitative PCR (qPCR). ****P<0.0001; vector versus FOXK1; FOXK1 versus FOXK1-c-jun siRNA. Scale bars represent 100 μm in (c) and 200 μm in (d). siRNA, small interfering RNA