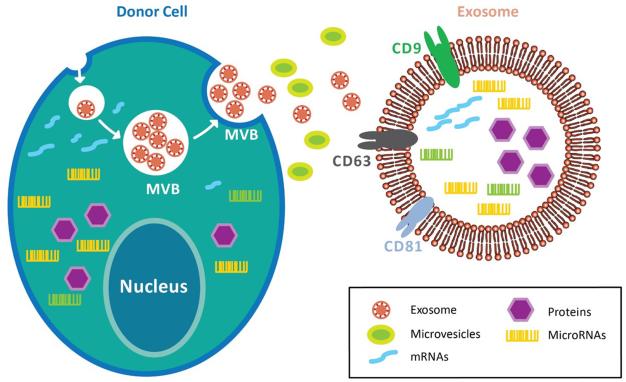
Figure 1. Biogenesis of exosome.
Exosomes are compartmentalized into the multivesicular bodies (MVBs), which fuse with the cell membrane and released to the extracellular space. This process prevents exosomes from degradation by the lysosomes. Exosomes comprise of various transmembrane and cytosolic proteins, such as integrins, CD9, CD63, and CD81. Furthermore, exosomes retain donor cells’ proteins, DNA fragments, miRNAs, and non-coding RNAs within the bi-lipid membrane. As such, exosomes preserve the genetic information of donor cells from enzymatic degradation while enabling targeted delivery of specific cargo.