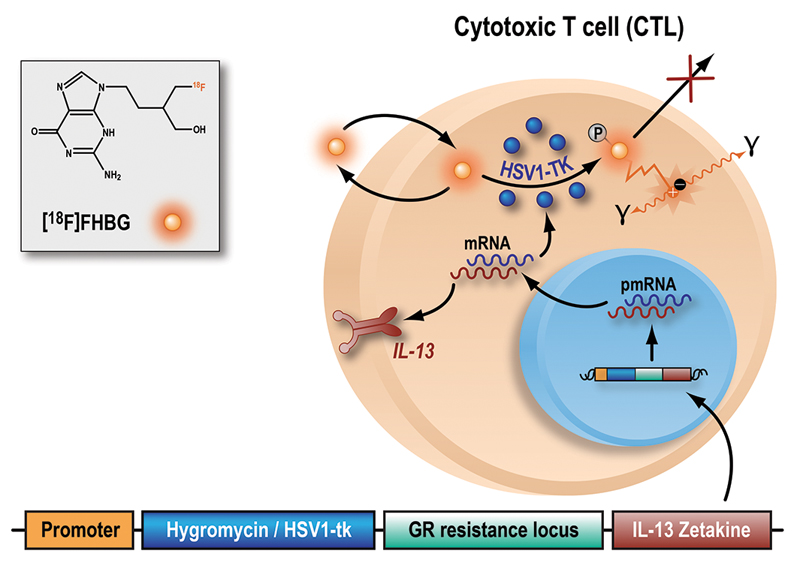
Fig. 1. The herpes simplex virus type-1 thymidine kinase gene (HSV1-tk) complex and monitoring by [18F]FHBG.
The herpes simplex virus type-1 thymidine kinase gene (HSV1-tk) complex is a genetically modified structure that was transfected into either autologous or allogeneic CTLs. This complex expresses a fusion protein consisting of a selective gene (hygromycin resistance locus) for adequate in vitro expansion of the CTL line; a PET reporter gene and safety gene, HSV1-tk; a glucocorticoid receptor (GR) resistance locus for improving CTL survival despite the high doses of steroids routinely given to high-grade glioma patients; and a IL-13 zetakine domain which is a chimeric receptor that enables glioma cell recognition by CTLs. CTL transfection was performed by electroporation. Inside the transfected cells, HSV1-tk is transcribed and translated to produce the HSV1-TK enzyme. [18F]FHBG is a labeled analog of penciclovir and substrate for HSV1-TK. In the presence of HSV1-TK, the radiolabeled probe is phosphorylated and trapped within the cell. The magnitude of [18F]FHBG signal reflects the activity of HSV1-TK enzyme and thus HSV1-tk gene expression. Abbreviation: pmRNA, pre-messenger RNA.