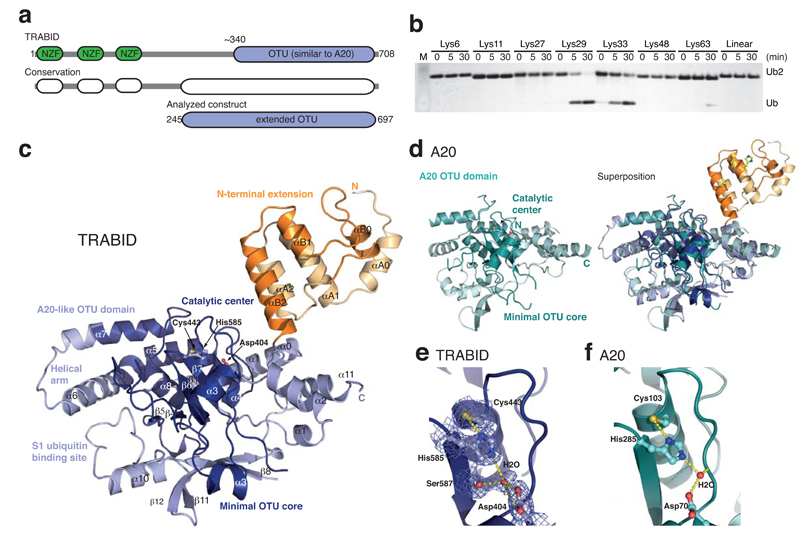
Figure 1.
Structure and specificity of an extended TRABID OTU domain. (a) Schematic representation of the functional domains of TRABID (top) and species conservation derived from a multiple sequence alignment (http://www.ensembl.org) (middle). An extended catalytic OTU domain was analyzed (aa 245-697, bottom). (b) Linkage specificity of the extended catalytic OTU domain of TRABID using diUb molecules of all eight linkage types, performed as reported before 26. TRABID was incubated with diUb for the indicated times, the reactions resolved on an SDS-PAGE gel and silver stained. (c) Structure of the extended TRABID OTU domain. The catalytic core is colored in shades of blue where dark-blue indicates the minimal OTU core domain, and lighter-blue additional secondary structure elements found in the A20-like subfamily of OTU DUBs. The Ank-repeats are shown in two shades of orange. The catalytic triad residues are indicated in ball-and-stick representation. (d) Structure of A20 (left, pdb-id 2vfj, 23) and superposition with TRABID (right). (e) Catalytic triad residues of TRABID are shown in ball-and stick representation with yellow sulfur, red oxygen and blue nitrogen atoms. A red sphere indicates a water molecule, and yellow dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonds. A 2|Fo|-|Fc| electron density map contoured at 1σ covers relevant residues. (f) The A20 catalytic triad shown as in e.