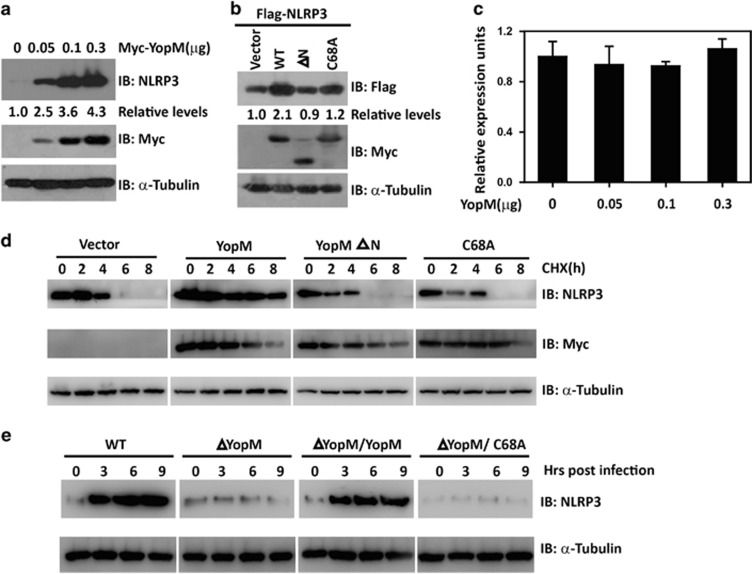
Figure 4.
YopM mediates the stabilization of NLRP3. (a) Immunoblotting analysis of extracts of HEK293 cells transfected with increasing doses of plasmid for YopM using anti-NLRP3 antibody. α-Tubulin was used as equal loading control. (b) Immunoblotting analysis of extracts of HEK293 cells transfected with plasmid for Flag-NLRP3 together with Myc-YopM, Myc-YopM ΔN, or Myc-YopM C68A showing NLRP3 stability. α-Tubulin was used as equal loading control. (c) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of NLRP3 mRNA levels in HEK293 cells transfected with increasing doses of plasmid for YopM. (d) HEK293 cells were transfected with the expression vector encoding Flag-NLRP3, Myc-YopM, Myc-YopM C68A or Myc-YopM ΔN. After 24 h, cells were treated with cycloheximide (10 μM) at the indicated time points, and the level of NLRP3 was monitored by immunoblotting using anti-Flag antibody. α-Tubulin was used as equal loading control. (e) BMDMs were infected with different background of Y. pestis. After infection, cell extracts were prepared at the indicated time points and subjected to immunoblotting. Cell-based studies were performed independently two to three times with comparable results