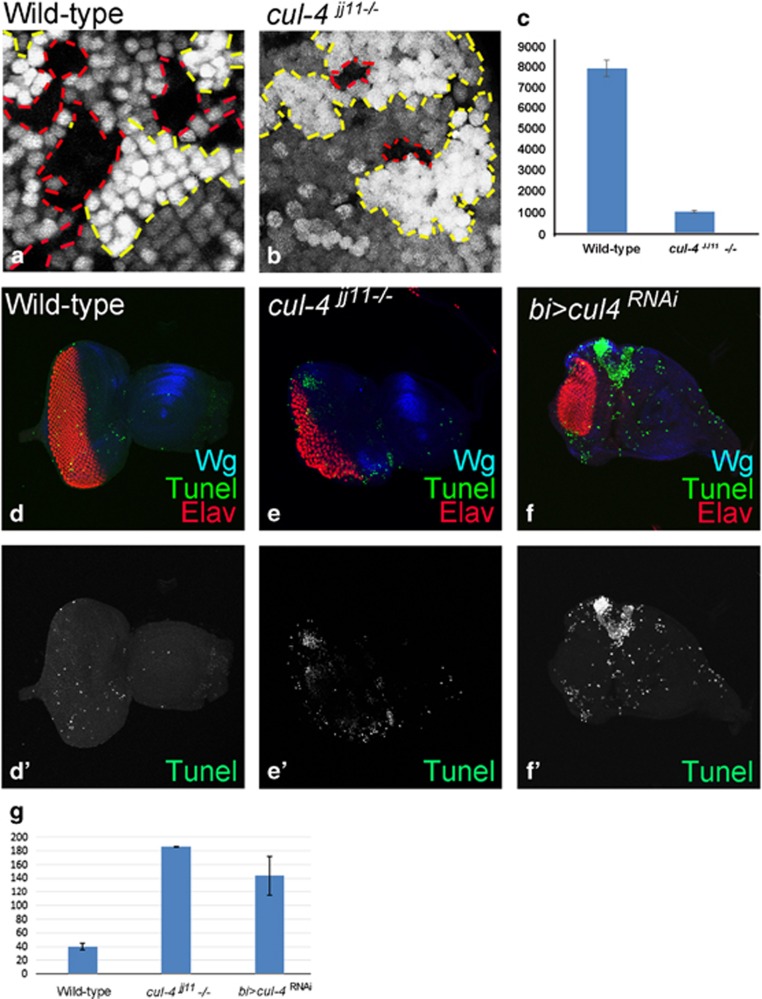
Figure 3.
Loss-of-function clones of cul-4 fail to survive. (a and b) Genetic mosaics generated by using a Flp-FRT system in the eye results in GFP-positive and GFP-negative patches of cells. (a) Note that in wild-type controls, clonal areas marked by the absence of GFP (red dotted lines) are comparable in terms of size to the wild-type clones (with strong (2X) GFP-positive areas, marked by red dotted lines). (b) Loss-of-function clones of cul-4JJ11 mutant in the eye imaginal disc (no GFP, marked by red dotted line) are smaller compared with the wild-type twin spot (2XGFP, marked by yellow dotted line). Note that these cul-4JJ11 mutant clones fail to survive 24 h after they are formed. Only GFP-positive (wild-type) cells were seen. (c)The cell number of cul-4 clones was less than eightfold as compared with the wild-type clones based on counting five eye discs for each. (d–f') TUNEL staining was used to mark the dying cells nuclei in (d and d') wild-type, (e and e') cul-4jj11−/− clones and (f and f') bi>cul4RNAi eye imaginal disc. (g) The dying nuclei were counted from five imaginal discs from each of these category. There is more than fourfold increase in dying cell population in cul-4 mutant eye disc as compared with wild-type