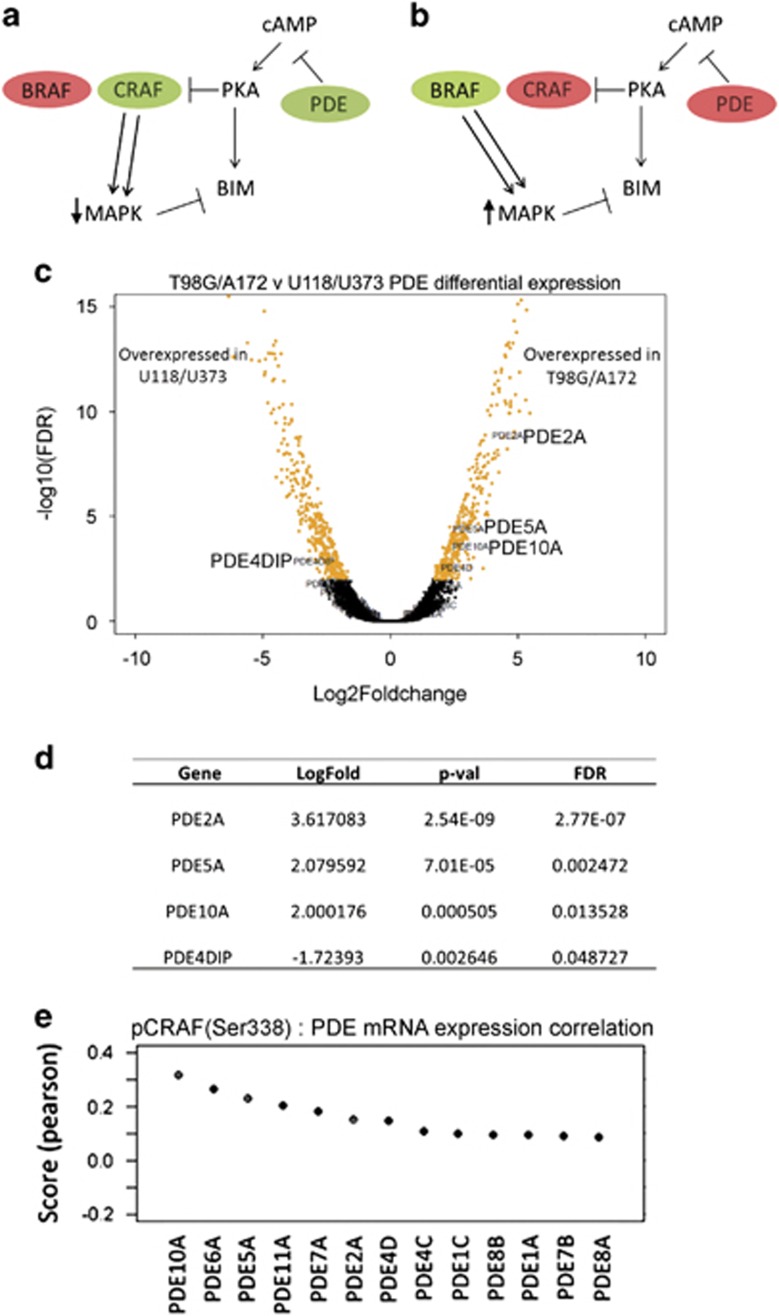
Figure 6.
Selective inhibition of pMAPK by cAMP agonists is dependent on RAF isoform dominance. Schema showing the mechanism of RAF isoform-dependent effects in relation to cAMP activation, MAPK pathway activity and BIM expression (modified from Marquette et al.23). (a) In cells where CRAF dominates, cAMP pathway activation can inhibit CRAF, downregulate MAPK activity and increase BIM expression. (b) In cells where BRAF dominates, BRAF is unaffected by cAMP signaling, so MAPK activity is high, which in turn inhibits BIM expression. (c) Volcano plot generated by gene expression analysis of the relative PDE expression comparing the cAMP-sensitive (T98G, A172) and -resistant (U118, U373) GBM cell lines. (d) The four PDEs showing the greatest differential expression between the cAMP-sensitive and -resistant GBM cell lines. (e) Co-expression analysis of CRAF phosphorylation and PDE subtype expression in GBM tumors shows that CRAF protein phosphorylation (phosphorylated at Ser338) is high in tumors with high PDE mRNA expression for 13 PDE subtypes examined. CRAF protein phosphorylation data was derived from TCGA reverse phase protein array (RPPA) data sets for GBM and PDE expression from TCGA GBM mRNA expression data sets