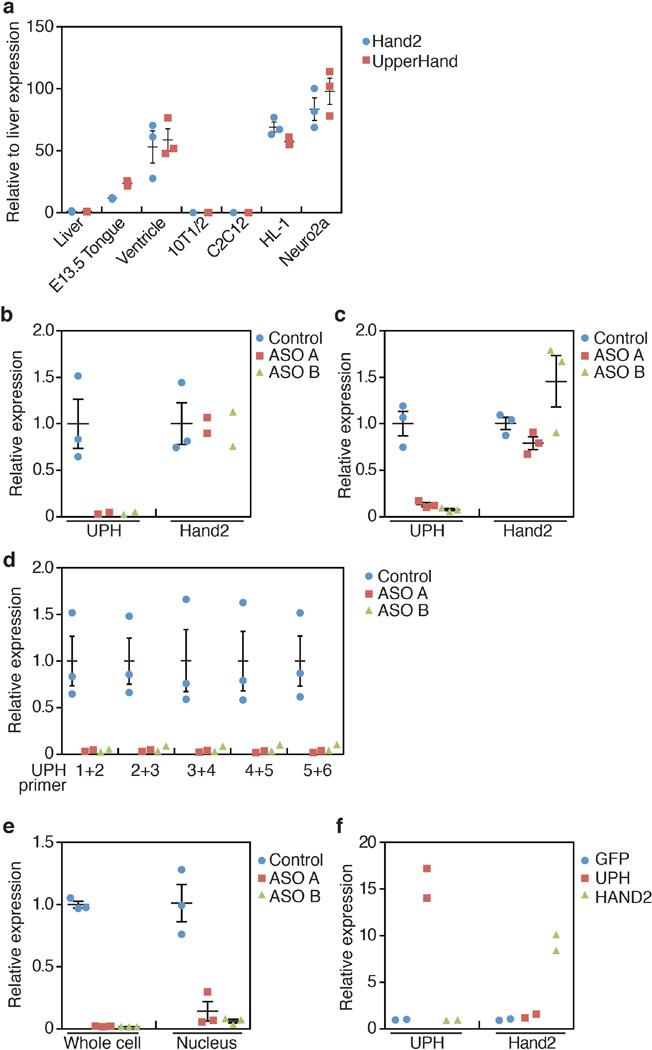
Extended Data Figure 6. Knockdown of mature Uph transcripts in HL-1 or Neuro2a cells does not affect Hand2 expression.
a, Expression of Uph (red) and Hand2 (blue) in various tissues and cell lines. Uph and Hand2 are robustly expressed in the heart, and the HL-1 and Neuro2a cell lines. Uph and Hand2 transcripts are not expressed in the liver, 10T1/2 fibroblasts or skeletal muscle C2C12 myotubes (n = 3 technical replicates; mean ± s.e.m.). b, c, Uph transcripts were reduced by ~90% in HL-1 (b) and Neuro2a (c) cells when transfected with two independent GapmeR antisense oligonucleotide probes (ASO A and B) against Uph. Expression of Hand2 was not changed (n = 2 for ASO A and B, n = 3 for control, from 1 of 2 independent experiments; mean ± s.e.m.). d, Uph transcripts were similarly downregulated across each exon–exon junction, measured using qPCR (n = 2 for ASO A and B, n = 3 for control, from 1 of 2 independent experiments; mean ± s.e.m.). e, Fractionation of HL-1 cells transfected with control or Uph-specific ASOs. The nuclear fraction of antisenseoligonucleotide-treated HL-1 cells showed a similar downregulation of Uph transcripts (n = 3 biological replicates from 1 of 3 independent experiments; mean ± s.e.m.). f, Overexpression of enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP; blue), the major Uph RNA (red) or Hand2 RNA (green) in HL-1 cells revealed that the mature Uph transcript did not alter Hand2 expression relative to wild type, and that Hand2 does not influence the expression of Uph in these cells (n = 2 biological replicates from 1 of 2 independent experiments; mean ± s.e.m.).